[Most Recent Entries] [Calendar View]
Wednesday, May 3rd, 2017
| Time | Event | ||||
| 10:05a | [Paleontology • 2017] Jianianhualong tengi • Mosaic Evolution in An Asymmetrically Feathered Troodontid Dinosaur with Transitional Features
Abstract Asymmetrical feathers have been associated with flight capability but are also found in species that do not fly, and their appearance was a major event in feather evolution. Among non-avialan theropods, they are only known in microraptorine dromaeosaurids. Here we report a new troodontid, Jianianhualong tengi gen. et sp. nov., from the Lower Cretaceous Jehol Group of China, that has anatomical features that are transitional between long-armed basal troodontids and derived short-armed ones, shedding new light on troodontid character evolution. It indicates that troodontid feathering is similar to Archaeopteryx in having large arm and leg feathers as well as frond-like tail feathering, confirming that these feathering characteristics were widely present among basal paravians. Most significantly, the taxon has the earliest known asymmetrical troodontid feathers, suggesting that feather asymmetry was ancestral to Paraves. This taxon also displays a mosaic distribution of characters like Sinusonasus, another troodontid with transitional anatomical features.
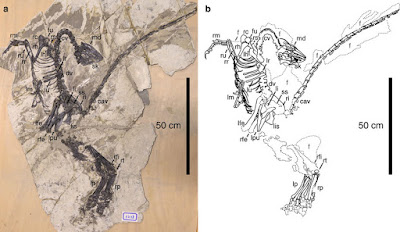
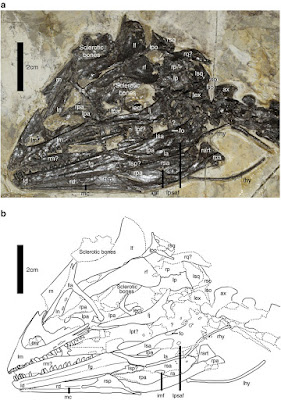
Systematic palaeontology Theropoda Marsh, 188121Coelurosauria Huene, 192022 Maniraptora Gauthier, 198623 Troodontidae Gilmore, 192424 Jianianhualong tengi gen. et sp. nov. Etymology. ‘Jianianhua’, the Chinese company that supported this study; ‘long’, the Chinese Pinyin for dragon. The specific name honors Ms Fangfang Teng, who secured the specimen for study. Holotype. DLXH 1218, a nearly complete skeleton with associated feathers (Fig. 1) housed at the Dalian Xinghai Museum. Locality and horizon. Baicai Gou, Yixian County, western Liaoning, China; Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation. Diagnosis. A troodontid distinguishable from other taxa in possessing the following apomorphic features (*indicates autapomorphic feature): maxillary rostral ramus triangular in outline and relatively high dorsoventrally*; maxillary ascending process extending posterodorsally at a high angle (an angle of ∼45° to maxillary ventral margin)*; lacrimal with a long descending process sub-equal in length to anterior process; a prominent ridge along anterior edge of the lateral surface of the lacrimal descending process; a distinct fossa on the dorsal surface of the surangular close to its posterior end; axial neural spine with a convex dorsal margin, transversely thickened anterior margin, and posterodorsal portion expanding strongly posteriorly; long manual phalanx II-1 (slightly shorter than metacarpal III) with prominent proximoventral heel, large groove along the medial surface of more than proximal half of manual phalanx II-1*; highly elongated manual III-2 (slightly longer than metacarpal III)*; robust ungual phalanges (medial ungual proximal depth/ungual length ratio >0.5); ilium with slightly concave dorsal margin in lateral view*; small medial lamina along ischial obturator process dorsal margin; metatarsal IV without prominent ventral flange*.  Xing Xu, Philip Currie, Michael Pittman, Lida Xing, Qingjin Meng, Junchang Lü, Dongyu Hu and Congyu Yu. 2017. Mosaic Evolution in An Asymmetrically Feathered Troodontid Dinosaur with Transitional Features. Nature Communications. 8, Article number: 14972. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14972 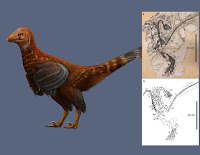  | ||||
| 10:10a | [Herpetology • 2017] Reinstatement of Varanus douarrha Lesson, 1830 As A Valid Species with Comments on the Zoogeography of Monitor Lizards (Squamata : Varanidae) in the Bismarck Archipelago, Papua New Guinea
Abstract The distribution and taxonomy of varanid lizards occurring in the Bismarck Archipelago is revised on the basis of field surveys, examination of museum vouchers and molecular phylogenetic analyses. A total of four species is recorded: Varanus indicus and Varanus finschi on New Britain and some of its offshore islands, Varanus douarrha on New Ireland, Lavongai and Djaul, and Varanus semotus on Mussau Island. V. douarrha, previously mistaken for both V. indicus and V. finschi, is shown to be the only species represented on New Ireland and is here resurrected as a valid taxon based on an integrated approach combining morphological and molecular evidence. Phylogenetic analyses of two mitochondrial genes suggest that V. indicus is a relatively recent immigrant to the Bismarck Islands, whereas V. douarrha, V. finschi and V. semotus have significantly longer histories in the island group. Together with the recently described V. semotus the revalidation of V. douarrha doubles the number of species known to occur in the Bismarck region and highlights an important component of both local and regional endemism. Keywords: endemism, neotype, New Ireland, taxonomy, Varanus indicus, Varanus finschi. Etymology: According to Lesson, the specific name douarrha was the local word for this species in Port Praslin. During fieldwork on New Ireland in 2012 VW interviewed a native speaker of the Siar-Lak language, which is what is spoken at Port Praslin. According to this local informant, the Siar-Lak word for ‘monitor’ is ‘kailam’. The word for the emerald tree skink, Lamprolepis smaragdina, is ‘dawar’, and it is possible that the words for these different species were confused by Lesson or that the application of local names has changed since his visit. Given current orthography for Siar-Lak (see en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Siar-Lak_language), it is clear that Lesson’s name was intended as a translitteration into French of the Siar-Lak name as he heard it.Words in Siar-Lak have the accent placed on the final syllable; hence, the name should be pronounced ‘dwah-rah’. Valter Weijola, Fred Kraus, Varpu Vahtera, Christer Lindqvist and Stephen C. Donnellan. 2017. Reinstatement of Varanus douarrha Lesson, 1830 As A Valid Species with Comments on the Zoogeography of Monitor Lizards (Squamata : Varanidae) in the Bismarck Archipelago, Papua New Guinea. Australian Journal of Zoology. DOI: 10.1071/ZO16038 Long lost monitor lizard 're-discovered' on Papua New Guinean island http://phy.so/412940372 @physorg_com |
| << Previous Day |
2017/05/03 [Calendar] |
Next Day >> |