[Most Recent Entries] [Calendar View]
Tuesday, January 22nd, 2019
| Time | Event | ||
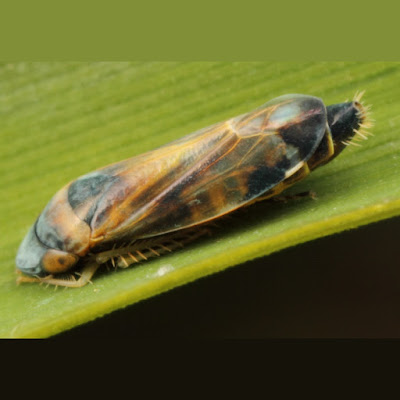
| 2:45a | [Entomology • 2019] Revision of the Bamboo Leafhopper Tribe Mukariini (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Deltocephalinae) from the Indian Subcontinent with Description of New Genera and Species
Abstract Leafhopper genera and species of the tribe Mukariini from the Indian subcontinent are revised. Nine genera and 22 species including two new genera, one new subgenus and 12 new species are dealt with. The new taxa described are Aalinga gen. nov. with its type species Aalinga brunoflava sp. nov. (India: Andaman Islands), Buloria indica sp. nov. (India: Karnataka). Buloria zeylanica sp. nov. (Sri Lanka), Flatfronta bella sp. nov. (India: Karnataka; Bangladesh), Mohunia bifurcata sp. nov. (Myanmar), Mukaria omani sp. nov. (India: Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh), Mukaria vakra sp. nov. (India: Karnataka), Mukariella gen. nov. with its type species Mukariella daii sp. nov. (India: Manipur), Myittana (Benglebra) cornuta sp. nov. (India: Karnataka), Myittana (Myittana) distincta sp. nov. (India: Karnataka), Myittana (Savasa) subgen. nov. with its type species Myittana (Savasa) constricta sp. nov. (India: Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand) and Scaphotettix arcuatus sp. nov. (India: West Bengal, Meghalaya, Mizoram). Genera Buloria Distant (new placement), Crispina Distant (new placement) and Myittana Distant (new placement) are placed in the tribe Mukariini. Genus Mohunia is redefined based on the study of its type species. Benglebra Mahmood & Ahmed 1969 is synonymised with Myittana Distant 1908 and considered as its subgenus. Myittana (Benglebra) alami (Mahmood & Ahmed) comb. nov., Myittana (Savasa) bipunctata (Mahmood & Ahmed) comb. nov.. Myittana (Benglebra) introspina (Chen & Yang 2007) comb. nov. and Mukariella bambusana (Li & Chen) comb. nov. are proposed; the first two species were earlier placed in the genus Benglebra, the third species in the genus Mohunia and the fourth in the genus Mukaria. Genera Flatfronta Chen & Li and Myittana are new records for India and Scaphotettix striata Dai & Zhang is a new record for the Indian subcontinent and Sri Lanka. All taxa dealt with are described and illustrated and keys for genera and their species are also given. Keywords: Hemiptera, Mukariinae, Buloria, Crispina, Myittana, bamboo, morphology C.A. Viraktamath and M.D. Webb. 2019. Revision of the Bamboo Leafhopper Tribe Mukariini (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Deltocephalinae) from the Indian Subcontinent with Description of New Genera and Species. Zootaxa. 4547(1); 1–69. DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.4547.1.1 | ||
| 3:35a | [Arachnida • 2019] Filling the Gaps: Descriptions of Unnamed Species included in the latest Molecular Phylogeny of Pholcidae (Araneae)
Abstract This paper provides formal descriptions of some of the unnamed taxa that were included in the most recent molecular phylogeny of pholcid spiders (Eberle et al. 2018, BMC Evolutionary Biology, 18, 141). The focus is on new genera and on species that belong to recently revised genera. Eight new genera and 25 new species are formally described. In Arteminae, three new species are described in Artema Walckenaer, 1837: A. bahla sp. n., A. ghubrat sp. n., and A. dhofar sp. n. (all from Oman); five new species in Arnapa gen. n. (eastern Indonesia and New Guinea): A. arfak sp. n., A. tinoor sp. n., A. manokwari sp. n., A. meja sp. n., A. tolire sp. n.; and one new species in Chisosa Huber, 2000: C. caquetio sp. n. (Netherlands Antilles). In Ninetinae, three new monotypic genera are described: Pemona gen. n., with the type species P. sapo sp. n. (Venezuela); Pinocchio gen. n., with the type species P. barauna sp. n. (Brazil); and Magana gen. n., with the type species M. velox sp. n. (Oman). In Modisiminae, three new species are described in Chibchea Huber, 2000 (all from Brazil): C. amapa sp. n., C. santosi sp. n., and C. hamadae sp. n.; one new species in Psilochorus Simon, 1893: P. bromelicolus sp. n. (Brazil); and three new monotypic genera, all from Brazil: Arenita gen. n., with the type species A. fazendinha sp. n.; Kairona gen. n., with the type species K. selva sp. n.; and Saciperere gen. n., with the type species S. catuaba sp. n. In Pholcinae, a new monotypic genus is described: Giloloa gen. n., with the type species G. sofifi sp. n. (Indonesia); three new species in the genus Aetana Huber, 2005 (all from Indonesia): A. ternate sp. n.; A. mokwam sp. n.; A. ondawamei sp. n.; and two new species in the genus Panjange Deeleman-Reinhold & Deeleman, 1983 (both from Indonesia): P. thomi sp. n., and P. togutil sp. n. Artema ghubrat is a cave-dwelling species and the only (slightly) troglomorphic representative of Arteminae; A. dhofar is presumably the closest known relative of the pantropical and synanthropic A. atlanta. The new genus Arnapa is probably species rich in eastern Indonesia and New Guinea but poorly collected; its morphological delimitation from other Australasian Arteminae (Wugigarra Huber, 2001; Holocneminus Berland, 1942; Trichocyclus Simon, 1908) needs further study. Arnapa nigromaculatus (Kulczyński, 1911) comb. n. is newly transferred from Psilochorus. Pemona sapo is the first representative of Ninetinae from Venezuela. The genus Chibchea, previously known from the Andes only, is for the first time recorded from Brazil/lowland Amazonia. Arenita fazendinha is among the few species in Pholcidae with extremely reduced procursus and barely modified male chelicerae. Kairona selva is unique among Pholcidae for its brush of strong hairs on a median horn anteriorly on the ocular area. Saciperere catuaba is one of only four pholcid species currently known to occur both in the Amazon and in the Atlantic Forest; however, variation indicates that more than one species might be included. It is among the few spiders known to have asymmetric genitalia (antisymmetric female internal genitalia). The Brazilian Psilochorus bromelicolus is the first South American Psilochorus of which both sexes are adequately described; however, the assignment to Psilochorus is tentative. Aetana ternate has extremely elongated procursi and accordingly elongated female internal genitalia. Aetana ondawamei and A. mokwam have almost identical male pedipalps and chelicerae (except for size) but differ clearly in the female genitalia. Keywords: Araneae, taxonomy, Pholcidae, Brazil, Oman, Indonesia Bernhard A. Huber and Leonardo S. Carvalho. 2019. Filling the Gaps: Descriptions of Unnamed Species included in the latest Molecular Phylogeny of Pholcidae (Araneae). Zootaxa. 4546(1); 1–96. DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.4546.1.1 Unnamed Species in Pholcidae Eight new genera and 25 new species are formally described. • Arteminae Artema Walckenaer, 1837: A. bahla sp. n., A. ghubrat sp. n., and A. dhofar sp. n. (all from Oman); Arnapa gen. n. (eastern Indonesia and New Guinea): A. arfak sp. n., A. tinoor sp. n., A. manokwari sp. n., A. meja sp. n., A. tolire sp. n.; one new species in Chisosa Huber, 2000: C. caquetio sp. n. (Netherlands Antilles). • Ninetinae, three new monotypic genera are described: Pemona gen. n., with the type species P. sapo sp. n. (Venezuela); Pinocchio gen. n., with the type species P. barauna sp. n. (Brazil); and Magana gen. n., with the type species M. velox sp. n. (Oman). • Modisiminae, three new species are described in Chibchea Huber, 2000 (all from Brazil): C. amapa sp. n., C. santosi sp. n., and C. hamadae sp. n.; one new species in Psilochorus Simon, 1893: P. bromelicolus sp. n. (Brazil); and three new monotypic genera, all from Brazil: Arenita gen. n., with the type species A. fazendinha sp. n.; Kairona gen. n., with the type species K. selva sp. n.; and Saciperere gen. n., with the type species S. catuaba sp. n. • Pholcinae, a new monotypic genus is described: Giloloa gen. n., with the type species G. sofifi sp. n. (Indonesia); three new species in the genus Aetana Huber, 2005 (all from Indonesia): A. ternate sp. n.; A. mokwam sp. n.; A. ondawamei sp. n.; and two new species in the genus Panjange Deeleman-Reinhold & Deeleman, 1983 (both from Indonesia): P. thomi sp. n., and P. togutil sp. n. | ||
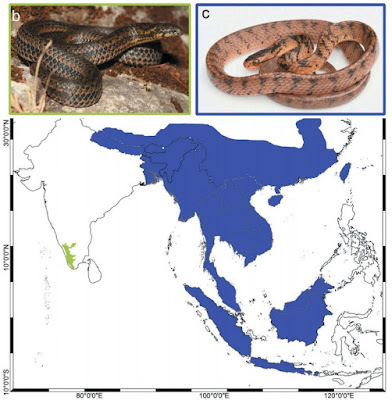
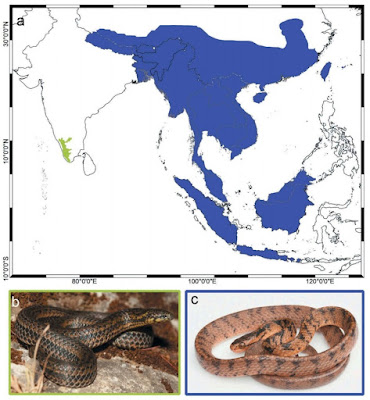
| 10:40a | [Herpetology • 2019] Xylophiinae subfam. nov. • A New Subfamily of Fossorial Colubroid Snakes from the Western Ghats of Peninsular India
ABSTRACT We report molecular phylogenetic and dating analyses of snakes that include new mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequence data for three species of the peninsular Indian endemic Xylophis. The results provide the first molecular genetic test of and support for the monophyly of Xylophis. Our phylogenetic results support the findings of a previous, taxonomically restricted phylogenomic analysis of ultraconserved nuclear sequences in recovering the fossorial Xylophis as the sister taxon of a clade comprising all three recognised extant genera of the molluscivoran and typically arboreal pareids. The split between Xylophis and ‘pareids’ is estimated to have occurred on a similar timescale to that between most (sub)families of extant snakes. Based on phylogenetic relationships, depth of molecular genetic and estimated temporal divergence, and on the external morphological and ecological distinctiveness of the two lineages, we classify Xylophis in a newly erected subfamily (Xylophiinae subfam. nov.) within Pareidae. KEYWORDS: Asia, classification, Pareidae, Pareinae, phylogenetics, Xylophis, taxonomy DIAPSIDA Osborn, 1903 Superorder LEPIDOSAURIA Haeckel, 1866 Order SQUAMATA Oppel, 1811 Suborder SERPENTES Linnaeus, 1758 Infraorder CAENOPHIDIA Hoffstetter, 1939 Superfamily COLUBROIDEA Oppel, 1811 Family PAREIDAE Romer, 1956 Subfamily Xylophiinae subfam. nov. Type genus: Xylophis Beddome, 1878 Content A single genus with three currently recognised species: X. stenorhynchus (Günther, 1875); X. perroteti Duméril, Bibron and Duméril, 1854; X. captaini Gower and Winkler, 2007. Xylophis indicus Beddome, 1878 has been considered a synonym of X. stenorhynchus (e.g. Smith 1943; Wallach et al. 2014) but might also be valid (Gower and Winkler 2007). Xylophis perroteti includes the synonyms Rhabdosoma microcephalum Günther, 1858 (e.g. Smith 1943; Wallach et al. 2014). Diagnosis Colubroid snakes with first (anteriormost) three pairs of infralabial shields reduced to narrow strips, together much smaller than large pair of anterior chin (genial) shields. Distribution The Western Ghats region of peninsular India. ... V. Deepak, Sara Ruane and David J. Gower. 2019. A New Subfamily of Fossorial Colubroid Snakes from the Western Ghats of Peninsular India. Journal of Natural History. 52(45-46) DOI: 10.1080/00222933.2018.1557756 |
| << Previous Day |
2019/01/22 [Calendar] |
Next Day >> |