[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
Below are the 2 most recent journal entries recorded in the "Сообщество, посвящённое ра" journal:| November 8th, 2012 | |
|---|---|
| 07:36 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
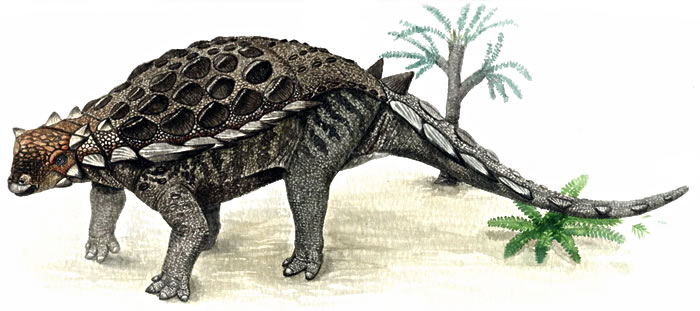
Mymoorapelta Mymoorapelta ("Shield of Mygatt-Moore") is an ankylosaur from the Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian-Tithonian) Morrison Formation (Brushy Basin Member) of western Colorado. The taxon is known from portions of a disarticulated skull, parts of three different skeletons and other postcranial remains. Present in stratigraphic zones 4 and 5 of the Morrison Formation. There is presently some controversy as to this ankylosaur's position within the Ankylosauria. Vickaryous et al. (2004) considered it Ankylosauria incertae sedis, while Kirkland et Carpenter (1994) placed it within the Family Polacanthidae. A new cladistic analysis performed by Thompson et al., 2011 suggests that Mymoorapelta is a basal nodosaurid. To date, only a single species has been named for this taxon, M. maysi. Along with Gargoyleosaurus parkpinorum, Mymoorapelta is one of the earliest known ankylosaurs, providing a look at the early evolution and diversification of this group of dinosaurs.
Ископаемые останки и реплики (1, 2, 3, 4):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Юра, авеметатарзалии, анкилозавры, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, динозавроморфы, динозавры, нодозавры, полакантины, птицетазовые, тиреофоры |
| October 21st, 2012 | |
| 06:38 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Gargoyleosaurus Gargoyleosaurus (meaning "gargoyle lizard") is one of the earliest ankylosaurs known from reasonably complete fossil remains. Its skull measures 29 centimetres (11 in) in length, and its total body length is an estimated 3 to 4 metres (9.8 to 13 ft). It may have weighed as much as 1 tonne (2,200 lb). The holotype was discovered at the Bone Cabin Quarry West locality, in Albany County, Wyoming in exposures of the Upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian stages) Morrison Formation. The type species, G. parkpinorum (originally G. parkpini) was described by Ken Carpenter et al. in 1998. A mounted skeletal reconstruction of Gargoyleosaurus parkpinorum can be seen at the Denver Museum of Nature and Science. Gargoyleosaurus was present in stratigraphic zone 2 of the Morrison Formation. The holotype specimen of Gargoyleosaurus parkpinorum was collected by Western Paleontology Labs in 1996 and is currently held in the collections of the Denver Museum of Nature and Science, Denver, Colorado. Besides the holotype, two other partial skeletons are known (although not yet described). The holotype consists of most of the skull and a partial postcranial skeleton. The specimen was originally described as Gargoyleosaurus parkpini by Carpenter, Miles and Cloward in 1998, then renamed G. parkpinorum by Carpenter et al. in 2001, in accordance with ICZN art. 31.1.2A. Much of the skull and skeleton has been recovered, and the taxon displays cranial sculpturing, including pronounced deltoid quadratojugal and squamosal bosses. The taxon is further characterized by a narrow rostrum (in dorsal view), the presence of seven conical teeth in each premaxilla, an incomplete osseous nasal septum, a linerarly arranged nasal cavity, the absence of an osseus secondary palate, and, as regards osteoderms, two sets of co-ossified cervical plates and a number of elongate conical spines. Vickaryous et al. (2004) place Gargoyleosaurus parkpinorum within the Family Ankylosauridae of the Ankylosauria and are in agreement with most previous phylogenetic hypotheses, which place the genus as the sister group to all other ankylosaurids (i.e., members of the Ankylosauridae). These studies however, only utilized the skull, whereas many of the distinctive features of the family Polacanthidae are in the postcranial skeleton. Анкилозавры (Ankylosauria — «согнутый ящер») — инфраотряд наземных динозавров отряда птицетазовых, характерной особенностью которых является костные образования на туловище. Передвигались на четырёх конечностях, питались растениями. Тело анкилозавров покрывал панцирь, состоящий из сросшихся костных щитков, шипов или спинных поясов, а на хвосте имелся костный вырост, который использовался для самозащиты. Жили анкилозавры в юрском и раннем меловом периодах на территории современных Европы, Северной Америки и Центральной Азии, в меловом периоде в Австралии и Антарктиде. В России обнаружены в верхнем мелу Амурской области. Нодозавриды (Nodosauridae) — семейство динозавров отряда птицетазовых, которые жили в период с позднего юрского и до конца мелового периода на территории современных Северной Америки, Азии, Австралии, Антарктиды и Европы. Семейство выделено в 1890 году Чарльзом Маршем и названо по типовому роду нодозавр (Nodosaurus). Одни из первых ископаемые нодозаврид, частичные останки левой лопатки (голотип USNM 8571) и несколько остеодермов (голотипы 8610 USNM, 8611) были отнесены к Scelidosauridae по Гилмор (1919); позднее останки лопатки были отнесены к роду Panoplosaurus (Lehman, 1981). В 2000 году Форд, основаясь на голотипе USNM 8610 поместил род Glyptodontopelta в новое подсемейство "Stegopeltinae" с Aletopelta и Stegopelta. Бернс (2008), в обзоре остеодермов анкилозавров, подтвердил законность Glyptodontopelta. Он поместил ее в семейство Nodosauridae, что делает подсемейство "Stegopeltinae" двусмысленным, из-за неопределенных сходств с Aletopelta. Исследования ученых показали, что нодозавриды произошли от общего предка тиреофоров. На сегодняшний день базальным членом данной группы является Antarctopelta, жившая около 74-70 млн лет назад. Однако одним из самых ранних нодозаврид является Sauropelta, жившая около 115 млн лет назад. В 2011 году был описан вид Propanoplosaurus marylandicus, который являетсяя единственным нодозавридом из раннего мела в восточной части США и является первым прямым доказательством того, что нодозавриды гнездовались на всем восточном побережье. Polacanthinae is a grouping of ankylosaurs, possibly primitive nodosaurids. Polacanthines are late Jurassic to early Cretaceous in age, and Kirkland observed they appeared to become extinct about the same time a land bridge opened between Asia and North America. Polacanthines were somewhat more lightly armoured than more advanced ankylosaurids and nodosaurids. Their spikes were made up of thin, compact bone with less reinforcing collagen than in the heavily armoured nodosaurids. The relative fragility of polacanthine armour suggests that it may have been as much for display as defense. The family Polacanthidae was named by Wieland in 1911 to refer to a group of ankylosaurs which seemed to him intermediate between the ankylosaurids and nodosaurids. This grouping was ignored by most researchers until the late 1990s, when it was used as a subfamily (Polacanthinae) by Kirkland for a natural group recovered by his 1998 analysis suggesting that Polacanthus, Gastonia, and Mymoorapelta were closely related within the family Ankylosauridae. Kenneth Carpenter resurrected the name Polacanthidae for a similar group which he also found to be closer to ankylosaurids than to nodosaurids. Carpenter became the first to define Polacanthidae as all dinosaurs closer to Gastonia than to either Edmontonia or Euoplocephalus. Most subsequent researchers placed polacanthines as primitive ankylosaurids, though mostly without any rigorous study to demonstrate this idea. The first comprehensive study of 'polacanthid' relationships, published in 2012, found that they are either an unnatural grouping of primitive nodosaurids, or a valid subfamily at the base of Nodosauridae.
Это преувеличение истинного размера тела животного. Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Юра, авеметатарзалии, анкилозавры, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, динозавроморфы, динозавры, нодозавры, полакантины, птицетазовые, тиреофоры |