[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
| February 29th, 2012 | |
|---|---|
| 07:28 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
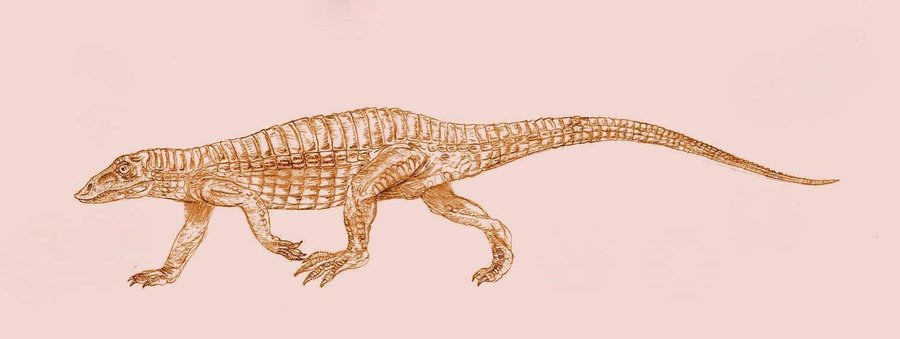
Aetosaurus Aetosaurus is an extinct genus of archosaur reptile belonging to the order Aetosauria. It is generally considered to be the most primitive aetosaur. Three species are currently recognized: A. ferratus, the type species from Germany and Italy; A. crassicauda from Germany; and A. arcuatus from eastern North America. Additional specimens referred to Aetosaurus have been found from South Africa, the Chinle Group of the southwestern United States, and the Fleming Fjord Formation of Greenland. Specimens of Aetosaurus occur in Norian-age strata. Aetosaurus was a small, primitive aetosaur. Unlike more derived aetosaurs such as Desmatosuchus or Typothorax, the carapace was long and narrow and lacked spikes. The paramedian scutes that covered the back (with one row on each side of the vertebrae) are considerably wider than they are long. The lateral scutes, which are beneath the paramedians and formed a row on either side of the animal, do not bear any spikes or other projections. Aetosaurus was first named with the description of the type species A. ferratus in 1877 by German paleontologist Oskar Fraas. At the time, Aetosaurus was known from 22 articulated skeletons that were found in the Lower Stubensandtein of Germany. Thirty years later, Fraas' son Eberhard described a second species, A. crassicauda, also from Germany. A. crassicauda can be distinguished from A. ferratus by its larger size; A. crassicauda reached a maximum length of 150 centimetres (59 in) while A. ferratus reached a length of up to 90 centimetres (35 in). In 1998, the genus Stegomus was synonymized with Aetosaurus. In 1896, paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh named Stegomus arcuatus from a cast of an aetosaur known as YPM 1647 from the New Haven Formation in Fairfield, Connecticut. This cast consisted of the dorsal carapace. Several other casts are known that preserve the surface of the skull and tail, and have been found from the Passaic Formation in Hunterdon and Somerset counties, New Jersey and the Lower Sanford Formation within the Triangle Brick Co. Quarry in Durham County, North Carolina. Stegomus arcuatus was found to be synonymous with Aetosaurus on the basis of several similarities, including a lack of spikes and a distinctive radial pattern of grooves on some of the caudal scutes. A. arcuatus has paramedian scutes that are much wider than they are long, even in comparison to other species of Aetosaurus. There is very little pitting on the surface of the scutes, although the porosity of the sandstone that makes up the casts has been mistaken for pitting. The tail narrows significantly past the base. The carapace is "waisted", meaning that it narrows in front of the pelvis. Aetosaurs (aetosaur Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can accurately date a site that they are found in. Aetosaur remains have been found since the early 19th century, although the very first remains that were described were mistaken for fish scales. Aetosaurs were later recognized as crocodile relatives, with early paleontologists considering them to be semiaquatic scavengers. They are now considered to have been entirely terrestrial animals. Some forms have characteristics that may have been adaptations to digging for food. There is also evidence that some if not all aetosaurs made nests.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, стагонолепидиды |