[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
November 23rd, 2014
| November 23rd, 2014 | |
|---|---|
| 01:43 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
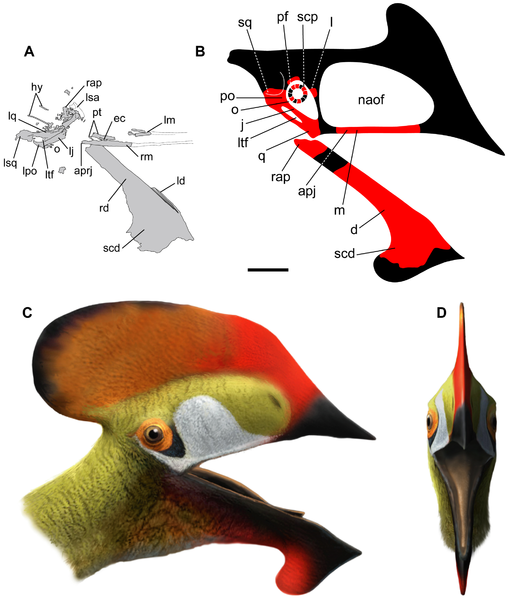
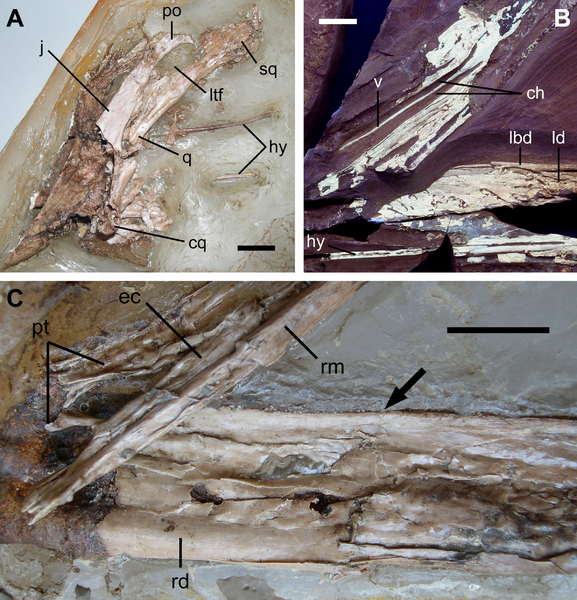
Caiuajara Caiuajara is an extinct genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Brazil. It is known from a single type species, Caiuajara dobruskii. In 1971, the labourers Alexandre Dobruski and his son João Gustavo Dobruski found pterosaur fossils in a field near Cruzeiro do Oeste in the south of Brazil, in the state of Paraná. The finds were in 2011 brought to the attention of paleontologists Paulo C. Manzig and Luiz C. Weinschütz. In 2014, the type species Caiuajara dobruskii was named and described by Paulo Manzig, Alexander Kellner, Luiz Weinschütz, Carlos Fragoso, Cristina Vega, Gilson Guimarães, Luiz Godoy, Antonio Liccardo, João Ricetti and Camila de Moura. The generic name refers to the geological Caiuá Group and the related genus Tapejara. The specific name honours the discoverers. The holotype, CP.V 1449, was found in a sandstone layer of the Goio-Erê Formation, the age of which is uncertain; it is perhaps dating from the Coniacian-Campanian, very roughly about eighty-five million years old. It consists of a partial skeleton including the skull, lower jaws, neck vertebrae and wing elements. Many hundreds of bones have been discovered, concentrated in several bone beds, and representing at least forty-seven individuals but probably many more. In the total assembly, all elements of the skeleton are present. The bones have been three-dimensionally preserved, not compressed, but are only rarely articulated. The individuals found are often juveniles; adult animals are much rarer, only represented by two skulls and three humeri. Good specimens have been assigned as paratypes, the more fragmentary ones have been referred. The paratypes are: CP.V 865: a snout, rear of the mandibula, right jugal, vertebrae, ribs and metatarsals; CP.V 867: a snout and limb bones; CP.V 868: a snout, wing elements and other postcrania; CP.V 869: a vertebral column, right arm, coracoid, breastbone, wing phalanges, belly ribs, pelvic elements and a right tighbone; CP.V 870: a shoulder girdle with the humeri; CP.V 871: a right shoulder girdle with right arm elements; CP.V 872: s partial skeleton including the skull, lower jaws, right arm, neck vertebrae and additional limb elements; CP.V 873: a snout and finger phalanges; CP.V 999: a partial skull; CP.V 1001: a slab with a partial skull, lower jaws and postcrania of at least three individuals; CP.V 1003: a partial skull and symphysis; CP.V 1004: a snout; CP.V 1005: a partial crested skull with the complete mandibula; CP.V 1006: a partial crested skull lacking the snout combined with postcrania; CP.V 1023: a snout and postcrania; CP.V 1024: a skull and postcrania of at least three juveniles; CP.V 1025: a thighbone; CP.V 1026: a thighbone; CP.V 1450: a slab containing at least fourteen juveniles; CP.V 2003: a skull with lower jaws and articulated wing elements; UEPG/DEGEO/MP-4151: a slab with two skulls and postcrania; and UEPG/DEGEO/MP-4152: a snout with postcrania. Most specimens are part of the collection of the Centro Paleontológico of the Universidade do Contestado. The largest individuals of Caiuajara had an estimated wingspan of 2.35 metres. The species had a large toothless head with, in adult individuals, an enormous shark fin-shaped crest on the snout. The describing authors established several distinguishing unique traits, autapomorphies. The tip of the snout is strongly oriented to below, at 142 to 149°, relative to the edge of the upper jaw. The rear ascending branches of the praemaxillae on their midline form an elongated bony rim projecting to below into the nasoantorbital fenestra, the large skull opening in the side of the snout. In the concave upper rear of the symphysis, the fronts of the lower jaws grown together, a rounded depression is present. The front outer edge of the quadrate shows a longitudinal groove. Below the front part of the nasoantorbital fenestra, a depression is present in the upper jaw edge. Additionally, Caiuajara shows an unique combination of traits that are themselves not unique. The lower edge of the eye socket is rounded. At a maximal occlusion, the gap between the upper and lower jaw is wider than with other tapejarines. The pteroid on its bottom surface shows a conspicuous depression lacking a pneumatic opening. Caiuajara was assigned to the Tapejaridae, more precisely the Tapejarinae. It shares several traits with the tapejarids, such as a crest running from the front snout to the back of the head; an elongated nasoantorbital fenestra occupying over 40% of total skull length; and a large boss on the front edge of the coracoid. A typical tapejarine trait is the down-turned snout tip. A cladistic analysis showed that Caiuajara is a possible sister species of Tupandactylus. In 2014, Caiuajara was the geologically youngest known tapejarid (aside from the possible tapejarid Bakonydraco galaczi) and also the most southern one known. This expansion of their known range was seen as an indication that tapejarids had a global distribution. Moreover, Caiuajara is the first pterosaur found in the south of Brazil. The habitat of Caiuajara was a desert with dunes. The layers in which the fossils were found had been deposited in a lake in the desert; probably the bones had been exposed at the surface around the lake for a time and were then by storms blown into it, eventually sinking to the bottom. Possibly the same storms caused many individuals to die together; this could also have been the result of droughts. A succession of layers shows that the lake was likely inhabited by the pterosaurs for a great length of time, although it is also possible they visited the lake during regular migrations. Fossil plants — tapejarids are often assumed to have been herbivores — have not been found, so there are no direct indications about the food source. Likewise, remains of invertebrates have not been discovered. The large concentrations of fossils, among pterosaurs very rare and only equalled by those found of the Argentine form Pterodaustro, were by the describers seen as proof of a gregarious lifestyle, Caiuajara living in colonies. The many specimens also allowed to determine a growth series, the first such an ontogenetic sequence for pterosaurs of which it is nearly certain that it really represented a single species. The age of the exemplars can be determined, not just from size but also by the degree of ossification, especially of the breastbone, the long bones and the wrist, and the fusion of the shoulder blade and coracoid into a scapulocoracoid. It showed that juvenile individuals, the smallest specimens of which have a wingspan of about sixty-five centimetres, generally had the same proportions as adults. Especially important is that their humeri are not proportionally smaller and their humeral deltopectoral crests, the attachments of the main flight muscles, are not less developed, attaining a size of 38 to 40% of the humeral shaft length. This suggests that they were precocial, taking wing almost as soon as they hatched; parental care must have been limited. This might have been typical of all derived pterosaurs. The snout crest however, strongly changed during growth. It became much taller and also much more steeply inclined, from about 115° to 90°. Although the snout as a whole also became more massive, the snout tip inclination relative to the jaw edge remained the same. At the back of the skull an additional projection developed. Furthermore the dentary crest on the lower jaw strongly increased in size. No specimens have been found lacking the snout crest, indicating that Caiuajara was in this respect not sexually dimorphic and casting doubt on the hypothesis that pterosaurs normally were. ( Read More ) Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4, 5):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, авеметатарзалии, аждархойды, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, монофенестраты, орнитохейройды, птеродактили, птерозавры, тапежариды |
| Time | Event |
| 03:34 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Europejara Europejara is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Spain. In 2012, the type species Europejara olcadesorum was named and described by Romain Vullo, Jesús Marugán-Lobón, Alexander Kellner, Angela Buscalioni, Bernard Gomez, Montserrat de la Fuente and José Moratalla. The generic name combines the names of Europe and the related genus Tapejara, in reference to the fact that Europejara is the first tapejarid found in that continent. The specific name refers to the Olcades, the Celtiberic tribe inhabiting the region of Cuenca, the location of the find, in Antiquity. The holotype, MCCM-LH 9413, was uncovered at the Las Hoyas site in a chalkstone layer of the Calizas de La Huergina Formation dating from the late Barremian. It consists of a partial skull with lower jaws, compressed on a slab and counterslab. Two elements of the hyoid are present also. The skull has been vertically crushed, the lower jaws horizontally. The specimen was prepared by Mercedes Llandres Serrano, and is part of the Las Hoyas collection of the Museo de las Ciencias de Castilla–La Mancha. Europejara is a relatively small form with an estimated wingspan of two metres. The jaws are toothless and the lower jaws bear a large downwards pointing crest. The describers established three autapomorphies, unique derived traits. The crest on the lower jaws is curved to the back. The crest is deeper than its base, measured from the front to the back, is wide. The crest is four times deeper than the back of the jaw. Two other diagnostic traits were indicated: the inner side of the lower jaw is thickened, causing a convex curvature; the inner side shows some shallow, but well-demarcated, depressions. Due to the crushing of the skull, its fragments, mainly representing elements from the area around the right eye socket, show little detail. The lower jaws have a preserved length of twenty-three centimetres and an estimated original length of 255 millimetres. In their front parts the lower jaws are fused by a symphysis into a mandibula. The symphysis has a concave upper profile and features a large crest on the underside, pointing downwards for at least nine centimetres. The back edge of the crest is recurved; the curvature of the front edge cannot be exactly established because of damage. The crest is the longest relative to lower jaw length of any known pterosaur. The internal bone structure of the crest is spongy. The rod-like first ceratobranchialia pair of the hyoid have a length of 135 millimetres and a cross-section of two millimetres. Europejara was assigned to the Tapejaridae. A cladistic analysis showed it to be more precisely a member of the Tapejarinae. Apart from being the first tapejarid known from Europe, it would also be the oldest pterosaur with certainty known to be edentulous; older fragments have been reported representing other generally toothless clades but these did not include the jaws themselves. Following earlier suggestions about the diet of tapejarids, the describers assumed a frugivorous lifestyle for Europejara. Because the species is so old it indicates a rôle for the tapejarids in the Cretaceous Terrestrial Revolution, a turn-over in the ecosystems of the Lower Cretaceous in which gymnosperms were replaced by angiosperms, flowering plants, and new groups of herbivores evolved, adapted to the changed food supply. In the case of tapejarids there could have been a reinforcing interactive cycle between the evolution of fruit and the pterosaurs dispersing the seed. Possibly the beaks of the tapejarids had ragged edges forming pseudo-teeth to better separate the fruit flesh from the seeds, as with some extant toucans. ( Read More ) Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, авеметатарзалии, аждархойды, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, монофенестраты, орнитохейройды, птеродактили, птерозавры, тапежариды |
| Time | Event |
| 08:09 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Ikrandraco Ikrandraco ("Ikran [a flying creature from Avatar with a crest on the lower jaw] dragon") is a genus of pteranodontoid pterosaur known from Lower Cretaceous rocks in northeastern China. It is notable for its unusual skull, which features a crest on the lower jaw. Ikrandraco is based on IVPP V18199, a partial skeleton including the skull and jaws, several neck vertebrae, a partial sternal plate, parts of both wings, and part of a foot. A second specimen, IVPP 18406, has also been assigned to Ikrandraco; it consists of a skull and jaws and the first three neck vertebrae. Both specimens come from the Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of Liaoning, with an estimated date of 120 million years ago. The type and only described species is I. avatar, a second reference to the movie Avatar. It was described in 2014 by Xiaolin Wang and colleagues. Ikrandraco is notable for having a very long, low skull (the height of the back of the skull, at the quadrates, is less than 19% the length of the skull), with a prominent blade-like crest on the underside of the lower jaw and no corresponding crest on the tip of the upper jaw, a crest combination not seen in other pterosaurs to date. The posterior edge of the crest also has a hook-like process. Each side of the upper jaw has at least 21 small cylindrical teeth, and each side of the lower jaw has at least 19. The skull of the type specimen is 286.5 millimetres (11.28 in) long, and the skull of the second specimen is at least 268.3 millimetres (10.56 in) long. Wang et al. performed a phylogenetic analysis including Ikrandraco and found it to be a basal pteranodontoid, more derived than Pteranodon but not as derived as the istiodactylids, anhanguerids, and other pteranodontoids. Wang et al. interpreted the crest as a possible adaptation for skim fishing, although they did not regard this as the animal's main method of foraging. The hook on the crest may have been an attachment point for a throat pouch for storing food, akin to a pelican. Ikrandraco was an approximate contemporary of distantly related anhanguerids Liaoningopterus gui and Guidraco venator, and all three are regarded as piscivores, but Ikrandraco differed from them in its much smaller and less robust teeth, indicating it had a different niche. ( Read More )</span>
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, авеметатарзалии, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, монофенестраты, орнитохейройды, птеранодонтойды, птеродактили, птерозавры |
| Time | Event |
| 09:52 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Banguela Banguela oberlii is a dsungaripterid pterosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Brazil. The Swiss collector Urs Oberli acquired a pterosaur jaw fragment from the Chapada do Araripe. In 2005, this was described by André Jacques Veldmeijer e.a. and referred to Thalassodromeus sethi. In 2006, Veldmeijer named it as a new Thalassodromeus species: Thalassodromeus oberli. However, this was done in his dissertation and thus merely resulted in an invalid nomen ex dissertatione. In 2014 it was named and described by Jaime Headden and Hebert Bruno Nascimento Campos as a separate genus Banguela, with the type species Banguela oberlii. The genus name is a Brazilian Portuguese word for "toothless one", especially used as an affectionate term for elderly women. The specific name honours Oberli. The holotype, NMSG SAO 251093, was probably found in the Romualdo Formation, also known as the Romualdo Member of the Santana Formation, dating from the Aptian-Albian. It consists of the symphysis, fused front end, of the lower jaws. Banguela has an estimated skull length of about two feet and wingspan of over twelve feet. The symphysis, with a preserved length of 273 millimetres, curves upwards and has a relatively short depression at its upper rear end. The front upper edge of the symphysis is sharp. The front bottom edge is sharp too but lacks a true crest. There are no teeth or tooth sockets present in the fragment. Veldmeijer had already in 2005 noted similarities to Dsungaripterus, but considered the available data to be insufficient to draw any conclusions from this. In 2014, Headden & Campos placed Banguela in the Dsungaripteridae, in a basal position. Banguela is unique among dsungaripterid pterosaurs due to a presumed total absence of teeth. Other pterosaur groups, such as pteranodontids, nyctosaurids and azhdarchoids, have also lost their teeth, indicating that toothloss might have independently occurred at least four times among pterosaurs. However, because dsungaripterids are occasionally recovered as derived azhdarchoids, it is possible that toothloss has occurred more often, if as an instance of Dollo's Law azhdarchoids should be originally toothless. If there was a large number of cases, Banguela suggests how it developed in most of these: the development of horned rhamphothecae in the jawtips, with progressive tooth rarification until they cease to be useful. It is worth to note that dsungaripteroids have some of the most specialised teeth of all sauropsids, so Banguela's toothlessness must indicate some degree of divergent specialisation.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, авеметатарзалии, аждархойды, архозавроморфы, архозавры, джунгариптероиды, диапсиды, монофенестраты, орнитохейройды, птеродактили, птерозавры |
| Previous Day | 2014/11/23 [Archive] |
Next Day |