[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
Below are the 5 most recent journal entries recorded in the "Сообщество, посвящённое ра" journal:| December 7th, 2013 | |
|---|---|
| 08:01 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
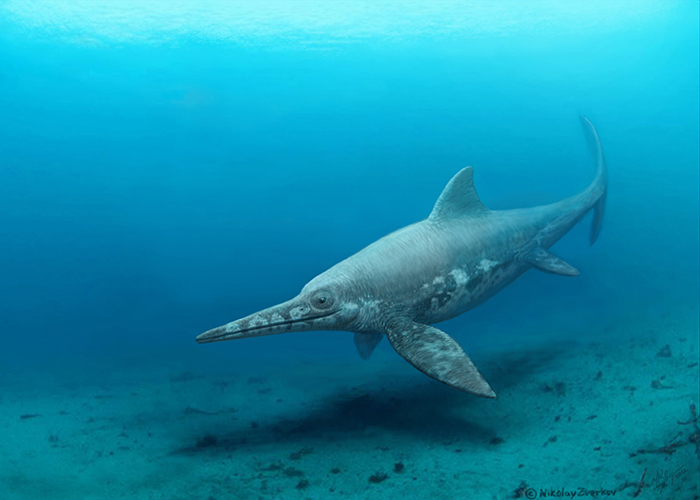
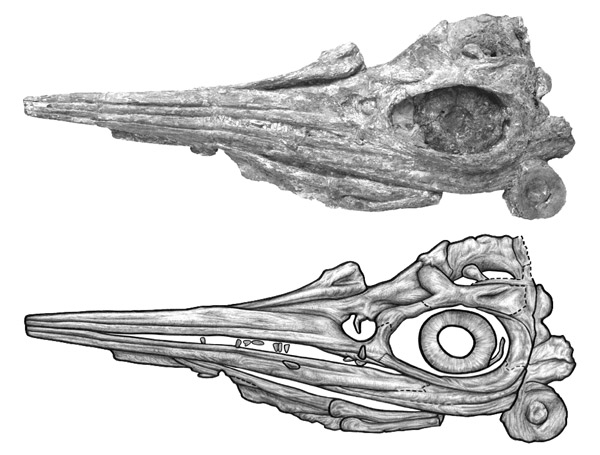
Sveltonectes Sveltonectes is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur known from Ul’yanovsk region, western Russia. Sveltonectes is known from the holotype IRSNB R269, an almost complete three-dimensionally preserved skeleton which preserved partial skull. It was collected in unnamed locality, in Ul’yanovsk, dating to the late Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous, about 126 million years ago. Another thunnosaur described from the same locality, by Bogolubow (1909), is "Ichthyosaurus" steleodon. It is a nomen dubium that is twice the size and more robust than Sveltonectes. Like some other ophthalmosaurids, Sveltonectes has a projection on the nasal bone of the skull into the naris, a prefrontal forming part of the margin of the naris and a frontal forming part of the margin of the supratemporal fenestra. Sveltonectes is unique in that it has small, sharp teeth and numerous other peculiar features such as a very primitive prootic. The distinctive shape of these teeth suggest that it had a different feeding habit than other cretaceous ophthalmosaurids. Within Ophthalmosauridae, Sveltonectes is most closely related to Aegirosaurus. Sveltonectes was named by Valentin Fischer, Edwige Masure, Maxim S. Arkhangelsky and Pascal Godefroit in 2011 and the type species is Sveltonectes insolitus. The generic name is derived from sveltos, Greek for "agile", and nektes, Greek for "swimmer", and refers to its small size, streamlined skull and powerful girdle musculature. The specific name is derived from insolitus, Latin for "unusual", in reference to the numerous unusual features of this ichthyosaur, as well as its unusual tooth morphology. Две интересные палеонтологические статьи, посвященные ихтиозаврам мелового периода, были опубликованы в конце 2011 и в начале 2012 годов. В этих публикациях описаны два новых рода ихтиозавров из России и Западной Европы, живших в меловом периоде. Обе находки стали доступны для изучения благодаря палеонтологам-любителям, хотя дороги, которые привели этих ихтиозавров в музеи, были очень разными. Возраст скелета удалось установить по раковинкам крошечных простейших – динофлагеллят, которые были найдены в породе, окружавшей череп ихтиозавра. Специалисты пришли к выводу, что обнаруженные виды динофлагеллят были характерны именно для баррема. Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, диапсиды, ихтиозавры, ихтиоптеригии, офтальмозавриды, платиптеригии |
| November 16th, 2013 | |
| 05:09 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
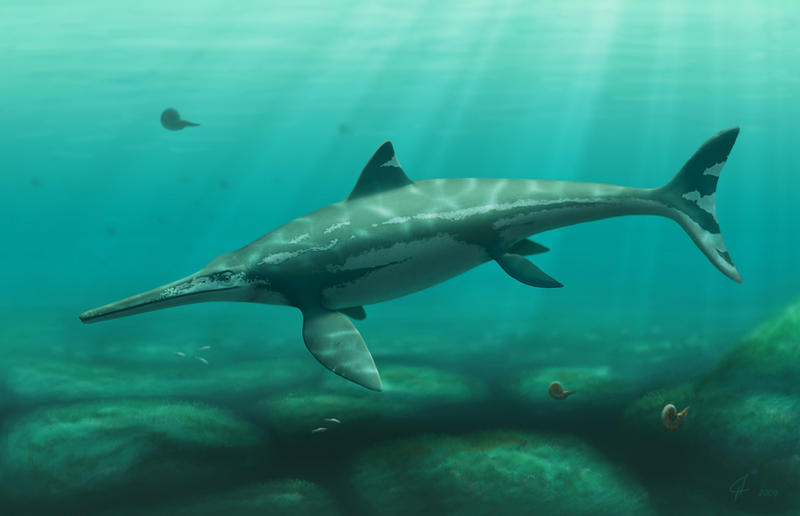
Platypterygius Платиптеригий (Platypterygius) — ихтиозавр мелового периода, последний по времени обитания из описанных по обнаруженным окаменелостям представителей группы. Крупный ихтиозавр, длиной до 9 метров. Череп низкий, с длинной мордой, небольшой орбитой, длинным посторбитальным отделом. Максилла чрезвычайно удлинена спереди. Зубы массивные, с квадратными в сечении корнями. Чешуйчатой кости нет. Септомаксилла окостеневшая. Затылочный мыщелок полусферический. Стремя массивное, с закругленной головкой (согласно некоторым исследованиям, животное было глухим). Первые три шейных позвонка срослись. В переднем плавнике чрезвычайно развита гиперфалангия и гипердактилия — число пальцев достигает 10). Фаланги в виде однообразных полигональных косточек. Тазовый пояс плохо известен, вероятно, редуцирован. Хвостовой плавник относительно невысокий, тело довольно длинное. Возможно, имелись какие-то органы кожной чувствительности (типа боковой линии) — на это может указывать структура костей черепа. Питался мелкой добычей (рыба, головоногие), что подтверждают и остатки содержимого желудка австралийского вида. Род широко распространен в первой половине мелового периода — с барремия по турон, известен как из Северного Полушария (Европа, Россия, Северная Америка), так и из Южного (Австралия и Аргентина). Не менее 11 видов, разделяемых на 4 подрода: Platypterygius, Longirostria, Tenuirostria, Pervushovisaurus. Типовой вид — P. (Platypterygius) platydactylus, из апта Германии, описан Бройли в 1907 году. Хорошо изучен австралийский вид P. (Longirostria) longmani из апта — турона Австралийского мелового моря. Это крупный (до 7 метров длиной) длинномордый вид. Первые остатки описаны как Ichthyosaurus austrialis МакКоем в 1867—1869 годах. Вид установлен М. Уэйдом в 1988 году. К роду может принадлежать также P. hercynicus из поздней юры Баварии. P. steleodon происходит из готерива-баррема Ульяновской области, описан по фрагментам челюстей и позвоночного столба. P. birjukovi известен по большей части черепа и позвоночного столба из баррема Ульяновской области. Отличается весьма крупными зубами. Орбиты низкие. Хорошо заметны вдавления на носовых костях (возможно, следы каких-то рецепторов). Длина черепа более 70 см. P. bedengensis описан по черепу и передней части скелета из готерива Ульяновской области. Длина около 5 метров. Чрезвычайно близок к австралийскому P. longmani, отличаясь деталями строения кисти. P. (Pervushovisaurus) bannovkensis — из среднего сеномана Саратовской области, описан по неполному черепу. Череп необычайно низкий и длинный, до 1,3 метра длиной. Орбиты низкие, сам череп уплощен. Рыло массивное, хорошо заметны ямки на ростре. Вероятно, последний из ихтиозавров, происходящий уже из позднемеловых отложений. Синонимы рода: Myobradypterygius, Myopterygius, Plutoniosaurus, Simbirskiasaurus. Платиптеригий интересен как последний по времени из классифицированных ихтиозавров и до недавнего времени, единственный из описанных меловых представителей группы. Австралийский и аргентинский виды могли обитать в относительно холодных полярных морях. Platypterygius ('Flat wing (flipper)', von Huene 1922) was an ichthyosaur of the family Ophthalmosauridae. It is most closely related to the genera Caypullisaurus and Brachypterygius. Fossils are known from Australia, Russia, United States of America, Colombia, Western Europe and possibly New Zealand. There are seven named species. Both adults and juveniles have been unearthed, including newborns and pregnant females. Like other ichthyosaurs, Platypterygius gave live birth. The remains from Australia were originally called Ichthyosaurus australis. They are from the Toolebuc Formation and Allaru Mudstone (Albian, Lower Cretaceous) of Flinders River and other localities in north central Queensland. In 1990 Wade erected the species name P. longmani to include all remains previously referred to I.australis . Platypterygius reached a length of about 7 m (23 ft). It had a long snout and a powerful finned tail. There are more digits in the front flippers than is usual in ichthyosaurs; they are tightly bound in rows, giving a broad, flat appearance. This unusual characteristic gives the genus its name, meaning 'flat wing.' Furthermore, some of the wrist bones have disappeared entirely. CAT scans on a juvenile specimen strongly suggest that Platypterygius was deaf. ( Read More ) Репродукции (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6):
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, диапсиды, ихтиозавры, ихтиоптеригии, офтальмозавриды, платиптеригии |
| April 9th, 2012 | |
| 08:33 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Caypullisaurus Caypullisaurus is an extinct genus of large platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous (Tithonian and Berriasian stages) of Argentina. Its holotype was collected from the Vaca Muerta Formation of Cerro Lotena, Neuquen, dating to the early Tithonian stage of the Late Jurassic, about 150 million years ago. Caypullisaurus was first named by Marta Fernández in 1997 and the type species is Caypullisaurus bonapartei. It is a member of the family Ophthalmosauridae, and closely related to Platypterygius and Brachypterygius. In 2012, Caypullisaurus was found to be most closely related to Athabascasaurus and "Platypterygius" australis, and to nest within the subfamily Platypterygiinae.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Юра, диапсиды, ихтиозавры, ихтиоптеригии, офтальмозавриды, платиптеригии |
| 08:24 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Brachypterygius Brachypterygius is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur known from England and European Russia. Brachypterygius was named by Friedrich von Huene in 1922 and the type species is therefore Brachypterygius extremus. The holotype of B. extremus is known from Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic of Kimmeridge Clay, area of Bath, England. McGowan, 1976 named a new genus of ichthyosaur, Grendelius mordax from Kimmeridgian stage of Kimmeridge Clay, Norfolk. In 1997, McGowan described additional specimens of the same taxon from the Kimmeridge Bay, Dorset, and referred it to a species of Brachypterygius. Efimov, 1998 named a new genus of ichthyosaur, Otschevia pseudoscythia on the basis of a single specimen (the holotype) from the Pseudoscythia Zone (late Tithonian stage of the Late Jurassic) of Ulyanovsk, Volga region, Russia. Later, Arkangelsky, 1998 described Brachypterygius zhuravlevi from a Tithonian-stage locality in Saratov, Russia. Maisch & Matzke, 2000 considered both russian taxa to be synonyms of each other, and referred the new combination B. pseudoscythius to Brachypterygius. Thus, Grendelius and Otschevia are considered to be junior synonyms of Brachypterygius. Brachypterygius is closely related to Platypterygius and Caypullisaurus. Maisch, 2010 also referred Ochevia alekseevi (named by Arkangelsky, 2001 from the late Jurassic of Russia) and an ichthyosaur from the Early Cretaceous of England to this genus.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Юра, диапсиды, ихтиозавры, ихтиоптеригии, офтальмозавриды, платиптеригии |
| 08:13 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Aegirosaurus Aegirosaurus is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur known from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Europe. Originally described by Wagner (1853) as Ichthyosaurus leptospondylus, it has had an unstable taxonomic history. It has also been named Ichthyosaurus trigonus posthumus, and identified with Macropterygius and Brachypterygius extremus. In 2000, Bardet and Fernández found that the holotype specimen of Macropterygius is undiagnosible, thus this genus is a nomen dubium. They selected a complete skeleton in a private collection as the neotype for this species, as the only other described specimen was destroyed in World War II. A second specimen from the Munich collection was referred to the same taxon. Bardet and Fernández concluded that the neotype should be assigned to a new genus, Aegirosaurus. The name means 'Aegir (teutonic god of the ocean) lizard with slender vertebrae'. Within Ophthalmosauridae, Aegirosaurus was regarded to be most closely related to Ophthalmosaurus. However, many recent cladistic analyses found it to be more closely related to Sveltonectes (and probably to Undorosaurus). Aegirosaurus lineage was found to include Brachypterygius and Maiaspondylus too, and to nest within Platypterygiinae which is the sister taxon of Ophthalmosaurinae. Aegirosaurus is known from the lower Tithonian (Upper Jurassic) of Bavaria, Germany. Its remains were discovered in the Solnhofen limestone formations, the same formations that have yielded numerous well-known fossils, such as Archaeopteryx, Compsognathus and Pterodactylus. In addition to its late Jurassic occurrence, Aegirosaurus has recently been discovered from the late Valanginian (Early Cretaceous) of Southeastern France (Laux-Montaux, department of Drôme; Vocontian Basin), the first diagnostic ichthyosaur recorded from the Valanginian. This shows that most types of Late Jurassic ichthyosaurs crossed the Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Юра, диапсиды, ихтиозавры, ихтиоптеригии, офтальмозавриды, платиптеригии |