[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
Below are the 6 most recent journal entries recorded in the "Сообщество, посвящённое ра" journal:| March 4th, 2012 | |
|---|---|
| 10:41 am [industrialterro] [Link] |
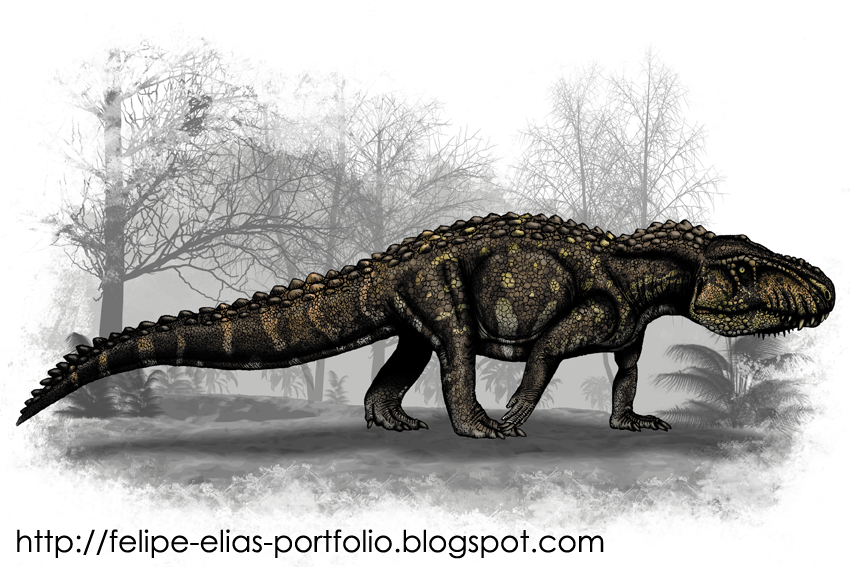
Ticinosuchus Ticinosuchus is an extinct genus of rauisuchian archosaur from the Middle Triassic (Anisian - Ladinian) of Switzerland and Italy. Ticinosuchus was about 3 metres (10 ft) long, and its whole body, even the belly, was covered in thick, armoured scutes. The structure of the hips shows that its legs were placed under the body almost vertically. Coupled with the development of a calcaneus and a specialized ankle joint, this would have made Ticinosuchus a fast runner, unlike most earlier reptiles.
Репродукции (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6):
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком и другими равизухиями (закрашен светло-зелёным цветом):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, престозухиды, равизухии |
| 10:01 am [industrialterro] [Link] |
Saurosuchus Saurosuchus (meaning "lizard crocodile" in Greek) is an extinct genus of rauisuchian archosaur in the family Prestosuchidae. With a length of around 7 m (23 ft), it was the largest rauisuchian, except perhaps for the less well known Fasolasuchus. Like other rauisuchians, Saurosuchus walked on four fully erect limbs. It lived in the Late Triassic of Argentina. Saurosuchus is known from several partial skeletons collected from the Ischigualasto Formation of Argentina. The holotype specimen consists of a complete but deformed skull, dorsal vertebrae, dorsal osteoderms, and parts of the pelvis. The hind limbs, tail, neck, and scapulae are also represented in several other skeletons. The type species S. galilei was named in 1959. Saurosuchus was also reported from the Chinle Formation of Arizona in 2002 on the basis of isolated teeth and small skull fragments. The diagnostic value of these bones has been questioned in later studies, which considered them to be from an indeterminate species of rauisuchian. Saurosuchus is one of the largest rauisuchians. The complete skeleton is not known and size estimates range from around 6 to 9 metres (20 to 30 ft) in total body length. It has a deep, laterally compressed skull. The teeth are large, recurved, and serrated. The skull is wide at its back and narrows in front of the eyes. The skull roof and maxilla are somewhat pitted, a distinguishing feature not seen in any other rauisuchian. Pitting is also seen in aquatic phytosaurs and crocodilians, but the ridges and grooves are deeper and much more extensive across the skulls of these forms. The frontal bones, located at the top of the skull, are enlarged to form thick ridges over the eyes. As in other rauisuchians, a small rod projects down from the lacrimal bone in front of the eye, but it does not attach firmly to the jugal bone below it. Ridges along the upper surface of the supraoccipital bone at the back of the skull are attachment points for strong neck ligaments. The cervical vertebrae are shortened and robust, forming a strong neck. Dorsal osteoderms run along the back of Saurosuchus. There are two rows to either side of the midline, with each leaf-shaped osteoderm joining tightly with the ones in front of and behind it.
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Размеры тела в сравнении с другими равизухиями (закрашен оранжевым цветом):
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, престозухиды, равизухии |
| March 2nd, 2012 | |
| 06:33 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Prestosuchus Престозух (Prestosuchus) — хищный архозавр триасового периода, представитель круротарзов. Относится к семейству Rauisuchidae или Prestosuchidae. Достигал в длину от пяти до семи метров. Крупный равизух, с высоким узким черепом. Предглазничное окно одно (заднее), средних размеров, расположено в глубоком вдавлении. Орбита в виде замочной скважины (глаз располагался в её верхней части, развито склеральное кольцо). Верхнее височное окно мелкое. Зубы максиллы разного размера, зазубренные, изогнутые, выделяются несколько крупных «клыков». Скелет массивный, таз трехлучевой. Лобковая кость короче седалищной. Вертлужная впадина закрытая. Пяточный сустав «нормально-крокодиловый». Пятая метатарзалия крючковидная, пятый палец стопы с одной фалангой. Конечности выпрямленные (парасагиттальное положение), животные четвероногие. Есть два ряда парамедианных остеодерм, соединенных передним отростком. В целом эта характеристика соответствует более примитивному строению, по сравнению с другими равизухами, следствием чего явилось выделение рядом исследователей семейства Prestosuchidae. Первые остатки престозуха были обнаружены Винсентом Престо в триасовых отложениях Чиниквы (формация Санта-Мария) в Бразилии в 1925 году. Это была нижняя челюсть, но там же находился целый скелет. В 1928 году Престо привел экспедицию Ф. фон Хюне к этому месту. К тому времени эрозия разрушила череп, но скелет был добыт. Род был назван фон Хюне в 1942 году (иногда указывают дату 1938 год) в честь В. Престо. Первоначально его систематическое положение было неясным и род сближали с этозаврами. Первые реконструкции скелета показывают низкий череп, что связано с недостаточной его сохранностью. Хюне описал сразу два вида: типовой P. chiniquensis и P. loricatus. Длина черепа типового вида около 60 см, общая длина — 4,8 метра. В 2000 году из среднего-позднего триаса Рио Гранде до Сул, на юге Бразилии был описан гигантский престозухид Karamuru vorax, с черепом 85 см длиной. К этому таксону отнесли, в частности, череп, ранее «принадлежавший» типовому виду престозуха. Систематическое положение этого гигантского хищника не определено до сих пор. Все виды происходят из среднего-позднего триаса (поздний ладиний — ранний карней), для Бразилии этому времени соответствует так называемая «терапсидная ценозона», характеризующаяся преобладанием крупных дицинодонтов. Именно они (в частности, шталекерия и динодонтозавр) представляли собой основную добычу престозухов. В карнейскую эпоху престозухов заменили ещё более крупные равизухии типа заврозуха и фазолазуха.
Репродукции (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9):
( Далее ) Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Размеры тела в сравнении с другими равизухиями (закрашен тёмно-синим цветом):
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6):
( Далее ) Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, престозухиды, равизухии |
| 06:22 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Karamuru Karamuru is a genus of prestosuchid archosaur from the Middle Triassic-age Santa Maria Formation of Brazil. It was found in the Paleorrota geopark. It is based on remains that had been assigned to Prestosuchus chininiquensis, including a nearly complete skull. There is some uncertainty about the publication date and authors; as noted by Langer et al. (2007), Kischlat (2000) records it as having been published by Kischlat and Barberena, with no year given. Later, Schultz and Langer considered it to be a junior synonym of Prestosuchus. Karamuru would have been a carnivorous animal, perhaps 7 meters long (23 ft) and weighing 700 kilograms (1500 lb). Its name relates to the story of Diogo Álvares Correia, a settler called the "Caramuru" by the Tupinambá tribe.
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, престозухиды, равизухии |
| 06:06 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Decuriasuchus Decuriasuchus is an extinct genus of prestosuchid rauisuchian from the Middle Triassic period (Ladinian stage). It is a carnivorous archosaur that lived in what is now southern Brazil. It was first named by Marco Aurélio G. França, Jorge Ferigolo and Max C. Langer in 2011 and the type species is Decuriasuchus quartacolonia. The generic name means "legion of ten crocodile" in Greek in reference to the ten known specimens and the animal's possible group behavior. The specific name refers to the Quarta Colonia region where the fossils were collected. Decuriasuchus is known from ten specimens, including nine articulated and associated skeletons, three of which have nearly complete skulls. The holotype MCN PV10105a consists of an articulated partial skeleton, lacking scapular girdle and limbs. Eight specimens associated with the holotype, MCN PV10105b-i, and the tenth specimen (MCN PV10004), consists of cranial remains from a different spot in the same locality. The specimens were found in the Alemoa Member of the Santa Maria Formation, Rosário do Sul Group. The discovery locality is Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Like other rauisuchids, Decuriasuchus was a quadrupedal carnivore that was one of the top predators of its environment. It grew to a length of around 2.5 metres (8.2 ft). Decuriasuchus is closely related to the genera Prestosuchus and Batrachotomus. A phylogenetic study of the genus placed it in the family Prestosuchidae, but found the Rauisuchia group to be paraphyletic. The study was based on an earlier 2010 analysis of archosaurs. As a rauisuchian, Decuriasuchus is a distant relative of modern crocodilians. Nine specimens of Decuriasuchus were found in close proximity to each other. A study of the taphonomy of the site (the conditions under which the skeletons became fossilized) indicates that the assemblage represents the single burial of multiple individuals rather than the collection of unrelated remains in one spot over a longer period of time. The congregation of nine individuals in one area suggests that they may have been traveling in a group. If this were the case, Decuriasuchus would be the earliest known archosaur to exhibit group behavior.
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Схема, показывающая расположение ископаемых скелетов относительно друг друга:
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, престозухиды, равизухии |
| 05:27 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
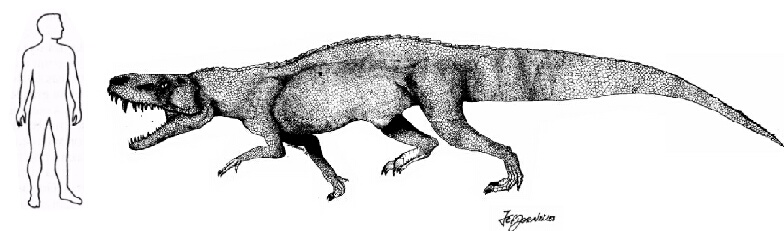
Batrachotomus Батрахотом (Batrachotomus) — хищный архозавр триасового периода, представитель круротарзов. Название в переводе на русский означает «лягушкорез». Относится к семействам Rauisuchidae, либо Prestosuchidae. Включает один вид — Batrachotomus kupferzellensis. Впервые был обнаружен в 1977 г. Иоганном Г. Вегелем возле Купферцелля (северный Баден-Вюртемберг, Южная Германия). Название связано с обнаруженными рядом костями мастодонзавров — предположительно основной пищей батрахотома. Описан Дэвидом Гоуером (David J. Gower) в 1999 году из среднего триаса (позднего ладиния — нижнего кейпера) Германии. Гигантское животное, не менее 6 метров длиной. Известно несколько частичных скелетов. Череп высокий, сжатый с боков, прямоугольных очертаний, длиной более 50 см. Ноздря больше предорбитального окна, есть вдавление на нижнебоковой поверхности посторбитальной кости. Сочленение между премаксиллой и максиллой включает в себя маленькое отверстие. Задний отросток премаксиллы короткий, максилла достигает ноздри. Верхний край носовых и предлобных костей черепа несет невысокие дорзолатеральные морщинистые гребни, есть невысокий сагиттальный гребень. У более крупных образцов гребень на костях черепа более выражен. Череп молодых особей более подвижен, у старых кинетика черепа почти утрачена. Зубы сжатые с боков, ножевидные, разного размера, некоторые — клыковидные. 3 крестцовых позвонка. Интерцентры позвонков отсутствуют. Есть «стопа» на лобковой кости. Лодыжка крокодиломорфная. Спинной панцирь состоит из двух рядов относительно узких скульптированных щитков, связанных передним отростком. В целом животное чрезвычайно сходно с равизухиями Южной Америки: престозухом и заврозухом. Определенные черты сходства наблюдаются и с североамериканским постозухом. Все эти гигантские наземные хищники были широко распространены в середине-конце триаса, до расцвета динозавров. Эти животные были четвероногими, прямоходящими (за счет смещения вертлужной впадины). Почти наверняка они охотились на суше. Сопутствующая фауна Купферцель-Бауэрсбаха включает мастодонзавра, капитозавра Kupferzellia, плагиозавров, трематозавра Trematolestes, метопозавра, двоякодышащих и лучеперых рыб. Всё это водные животные, но не исключено, что наземный компонент фауны просто пока не известен. В последнее время появились сообщения о находке в местонахождении антракозавроморфа Bystrowiella, этозавров, мелкого «текодонта», сходного с эупаркерией. Prestosuchids were a group of Triassic carnivorous archosaurs. They were large active terrestrial apex predators, ranging from around 2.5 to 7 metres (8.2 to 23 ft) in length. They succeeded the Erythrosuchidae as the largest archosaurs of their time. While resembling erythrosuchids in size and some features of the skull and skeleton, they were more advanced in their erect posture and crocodile-like ankle, indicating more efficient gait. Prestosuchids flourished throughout the whole of the middle, and the early part of the late Triassic, and fossils are so far known from Europe, India, Africa (Tanganyika), Argentina,and Paleorrota in Brazil. However, experts disagree regarding the phylogenetic relationships of the group, what genera should be included, and whether indeed the Prestosuchidae constitute a distinct family apart from the Rauisuchidae. 1957, Alan Charig proposed a new family, the Prestosuchidae, to include genera like Mandasuchus, Prestosuchus, and Spondylosoma. In 1967, Alfred Sherwood Romer placed Saurosuchus and Rauisuchus within Erythrosuchidae and adopted the Prestosuchidae to include Prestosuchus, Procerosuchus, and Charig's "Mandasuchus". Prestosuchidae have often been included within Rauisuchidae, although they have sometimes considered the sister group of the aetosaurs in a monophyletic Pseudosuchia, or as a small clade intermediate between basal Crurotarsi and more advanced archosaurs such as the Aetosauridae and Rauisuchidae. J. Michael Parrish's 1993 cladistic analysis of crocodylotarsan archosaurs places the Prestosuchidae (including Prestosuchus, Ticinosuchus, and Saurosuchus) outside the crocodylomorph - poposaurid - rauisuchid - aetosaur clade. In most cladograms Prestosuchids are considered more derived than phytosaurs and ornithosuchids, but usually less derived than the poposaurids and aetosaurs. The earliest known prestosuchid is Mandasuchus from the Anisian of Tanganyika. This was already a large animal, about 4.75 meters long. A similar but smaller form (perhaps the same genus) is Ticinosuchus of the Middle Triassic (Anisian-Ladinian) of Switzerland and Northern Italy, which was about 2.5 meters in length. The huge (6 meters long) Batrachotomus from the latest Middle Triassic (Late Ladinian) of Germany, and Prestosuchus of the early Late Triassic (Carnian) of Brazil may have been closely related animals. Yarasuchus was a lightly built animal from the Middle Triassic of India that also seems to belong to this group. Finally, Saurosuchus was a huge carnivore, 6 or 7 meters long, whose fossils are known from the Late Carnian of Argentina.
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком и другими равизухиями (закрашен светло-синим цветом):
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4, 5):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, архозавроморфы, архозавры, диапсиды, круротарзы, престозухиды, равизухии |















.jpg224fe0c2-1f3a-4ef1-92af-3dda974cabceLarger.jpg)























/Batrachotomus_1.jpg)


