[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
Below are the 7 most recent journal entries recorded in the "Сообщество, посвящённое ра" journal:| November 3rd, 2013 | |
|---|---|
| 06:50 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
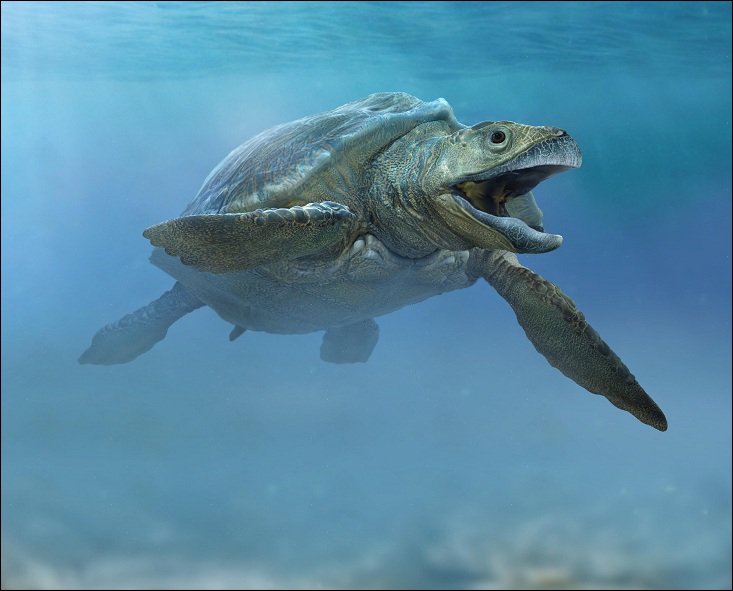
Ocepechelon Ocepechelon is an extinct genus of giant dermochelyoid sea turtle known from Late Cretaceous (late Maastrichtian stage, 67 Myr) Phosphatic deposits of the Oulad Abdoun Basin, Khouribga Province of Morocco. It is known from the holotype OCP DEK/GE 516, a complete but isolated 70-cm-long skull, making it one of the largest marine turtles ever described. It was first named by Nathalie Bardet, Nour-Eddine Jalil, France de Lapparent de Broin, Damien Germain, Olivier Lambert and Mbarek Amaghzaz in 2013 and the type species is Ocepechelon bouyai. The feeding apparatus of Ocepechelon, a bony pipette-like snout, is unique among tetrapods and shares unique convergences with both syngnathid fishes (unique long tubular bony snout ending in a rounded and forward directed mouth) and beaked whales (large size and elongated edentulous jaws. The removal of outgroup taxa, except the hypothetical taxon, resolved some relations and found Ocepechelon and Bouliachelys to be basal dermochelyoids in a polytomy with the Dermochelyidae and the Protostegidae. The inclusion of Chelomacryptodira resolved this polytomy, and found Ocepechelon to be the most basal dermochelyid. Гигантская морская черепаха, жившая 70 млн лет назад у побережья Африки, обладала уникальным ротовым аппаратом, напоминающим пипетку. До сих пор ничего подобного палеонтологам у рептилий не встречалось. ( Read More )
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, диапсиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |
| 05:00 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
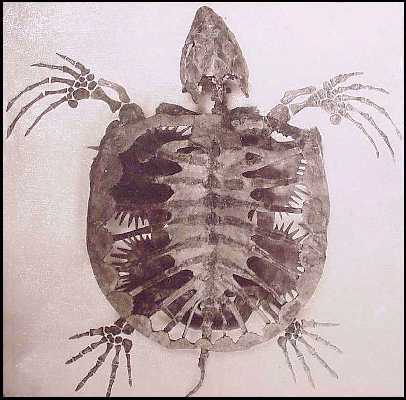
Toxochelys Toxochelys (TOKS uh KEE leez) is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas. Toxochelys was about 2 m (6 ft) in length. There are four known species in the genus: Toxocheys bauri, Toxochelys browni, Toxochelys latiremus, and Toxochelys weeksi. Phylogenetic analysis shows that Toxochelys belong to an extinct lineage of turtles transitional between modern sea turtles and other turtles.
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, диапсиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |
| October 27th, 2013 | |
| 01:53 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
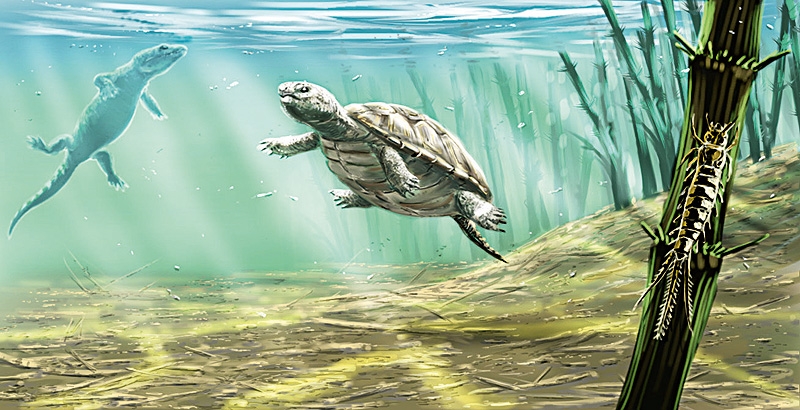
Santanachelys Santanachelys gaffneyi is the earliest known sea turtle. It is the only species in the genus Santanachelys, which itself is a member of the extinct family Protostegidae. The species was first described from a 20-centimeter long fossil specimen unearthed in 1998 in Eastern Brazil. Due to the rock layer from which it was excavated, it was determined that the specimen was from the Early Cretaceous period some 110 million years old. While the specimen showed many characteristics of modern sea turtles, it differed from the typical sea turtle body plan in several ways. One glaring difference is that Santanachelys had distinguishable digits at the tip of its forearms. Instead of the fully fused, hydrodynamic paddles that modern sea turtles possess, the early sea turtle's digits were distinct and movable similar to that of non-marine turtles. Like later sea turtles though, Santanachelys had large salt glands situated near its eyes which allowed it to drink saltwater without dehydration. Evolutionarily, the morphology of Santanachelys is typical of what is expected of an early sea turtle. The front appendages not being fully evolved into flippers is a sign of this. The presence of large foramen in the turtle's skull where salt glands were is an interesting evolutionary point. It is pointed out that this suggests that the evolutionary return to oceanic waters of the sea turtle line evolved before the finalization and streamlining of the line's paddles. Taxonomically, Santanachelys has been placed in the family Protostegidae along with many other extinct sea turtles. It is the earliest member of the family to date, and the earliest known member of the sea turtle superfamily, Chelonioidea. Cladistically, it is the sister taxon to the rest of the later protostegids, including Protostega and Notochelone. As a member of its family, its closest living relative belongs to the family Dermochelyidae, the leatherback turtle. Its genus, Santanachelys was named for the Santana Formation, the locality where the fossil was found and chelys, Greek for "turtle". The species name, S. gaffneyi was named in honor of Eugene S. Gaffney, a paleontologist who specialized in turtle phylogeny.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, бесщитковые, диапсиды, протостегиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |
| June 24th, 2013 | |
| 08:13 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
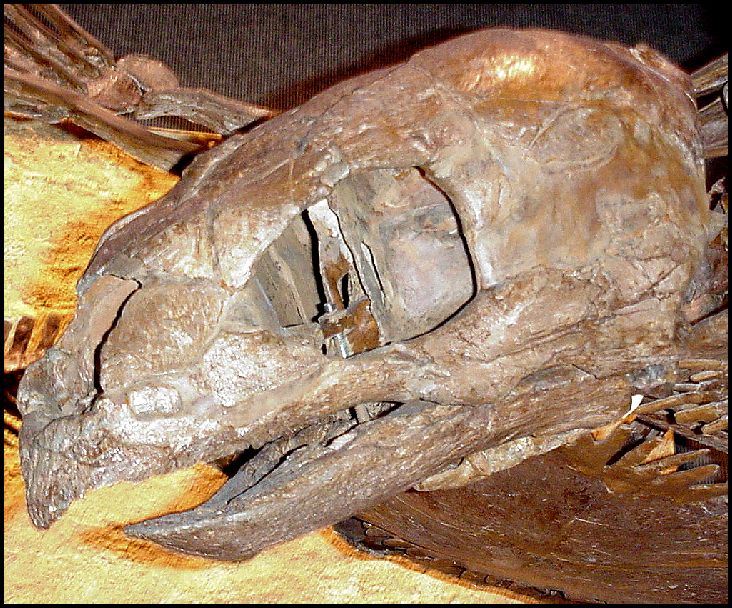
Protostega Протостега (Protostega) — гигантская морская черепаха мелового периода. Принадлежит к вымершему меловому семейству Protostegidae, близкому к современным кожистым черепахам. Описана Э. Д. Коупом в 1872 году на основании остатков пластрона, найденных в 1871 году в канзасских меловых отложениях. Гигантская черепаха, длиной до 3,4 метров, но обычные размеры около 2—2,5 метров. Отличается относительно крупными размерами черепа, ширина черепа почти равна длине. Клюв слабо загнут вниз и не так выделяется как у архелона. Широкая альвеолярная поверхность верхней челюсти простирается почти до глазницы. Очень мощный латеральный отросток плечевой кости. Невральный киль неровный. Реберные пластинки относительно развиты, фонтанели в карапаксе меньше, чем у архелона. Краевые пластинки ровные. Кости пластрона крупные, брюшная фонтанель небольшая. Ласты относительно короче, чем у архелона. Происходит из более древних отложений, чем архелон, входит в фауну Ниобрары (коньяк-сантон). Известна из Канзаса, Южной Дакоты, Колорадо, Вайоминга, Алабамы, Миссури, Техаса. Не исключено существование этого рода и вне Северной Америки (например, в верхнем мелу Англии или Восточной Азии, также Марокко). Типовой вид — P. gigas. Указывается на существование не менее 5 видов, которые могут быть синонимами типового. По образу жизни могла отличаться от архелона, ввиду различий в строении черепа. Возможно, питалась моллюсками, может быть, даже водорослями. Также как и для архелона, известны остатки скелетов со следами зубов акул (и самими зубами, застрявшими в кости). Вероятно, акулы объедали мертвых черепах. Известны случаи, когда задние ласты протостегид принимали за «скелет руки человека мелового периода», что активно используют в своих целях креационисты. Protostega gigas ('first roof' - 'giant') is an extinct species of marine turtle. It was first collected from the Smoky Hill Chalk of western Kansas in 1871, and named by E.D. Cope (1872). With a length of 3 m (10 ft), it is the second-largest turtle that ever lived, second only to the giant Archelon. Like the modern leatherback sea turtle, the largest living turtle at 2.70 m (9 ft) long, Protostega's carapace lacked scutes, making it weaker but also lighter. Protostega probably fed on slow ocean creatures such as jellyfish and shellfish.
Протостега улепётывает от кретоксирины.
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4, 5):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, бесщитковые, диапсиды, протостегиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |
| 07:25 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Notochelone Notochelone is an extinct genus of sea turtle, which existed about 100 million years ago. The species was first described by Richard Lydekker in 1889. It was the most common marine reptile living in the inlands of the sea around Queensland, Australia. It was a small turtle, and was about the same size as the modern green turtle. Analytical studies have indicated that the creatures frequently ate benthic molluscs.
Размеры тела, в сравнении с человеком и другими протостегидами (закрашена бирюзовым цветом):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, бесщитковые, диапсиды, протостегиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |
| June 10th, 2013 | |
| 08:55 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
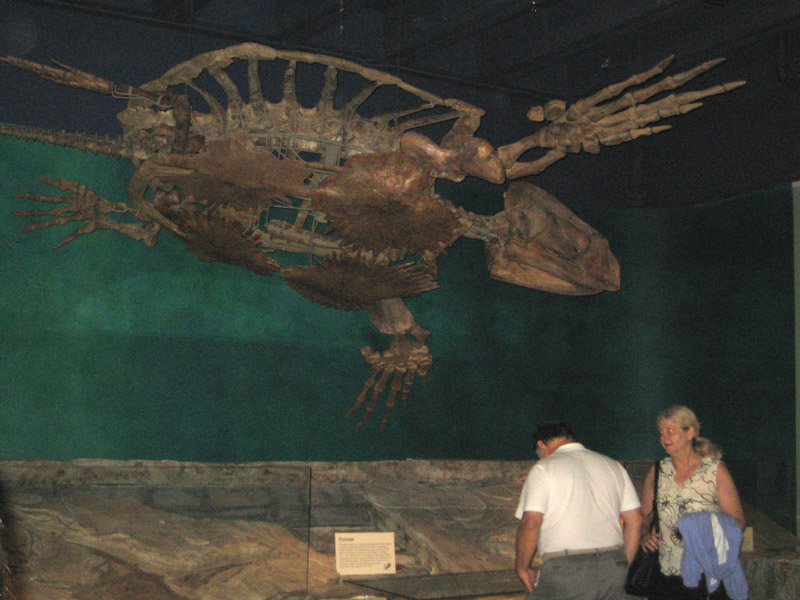
Archelon Архелон (Archelon ischyros) — гигантская морская черепаха мелового периода. Самая крупная из известных черепах. Принадлежит к вымершему меловому семейству Protostegidae, близкому к современным кожистым черепахам. Общая длина до 4,6 метров, вес более 2,2 тонн. Передние ласты огромные, крыловидные, служили основным органом передвижения. Размах ластов достигал 5 метров. Длина черепа до 70 см (превышает ширину). Клюв огромный, загнутый (напоминает клюв хищной птицы). Альвеолярная поверхность клюва не заходит назад дальше хоан. Латеральный отросток плечевой кости слабый. Панцирь редуцирован, хотя и в меньшей степени, чем у современной кожистой черепахи. Сохраняется ряд невральных пластин вдоль позвоночника, возможно, с кожными окостенениями над ними. Срединный киль панциря невысокий, непрерывный. Пластрон с большими звездчатыми пластинами, в количестве четырех, между ними — центральная фонтанель. Панцирь не такой плоский, как изображали на старых рисунках, несколько сходен с панцирем современных зелёных черепах по общему виду (за вычетом отсутствия роговых пластинок). При жизни панцирь был покрыт толстой кожей (как у современных взрослых кожистых черепах). Впервые описана Вейландом в 1896 году. Все экземпляры происходят из позднего мела (кампан) Северной Америки. Входит в поздний фаунистический комплекс Пьер Шейл. Остатки, включая полные скелеты, обнаружены в Южной Дакоте и, возможно, в Вайоминге. Интересны находки скелетов с прижизненными повреждениями — например, у типового скелета в Йельском Музее отсутствует правый задний ласт. Предполагается, что он был откушен при жизни акулой, либо мозазавром. Находки полных скелетов протостегид иногда объясняют тем, что черепахи могли зарываться в ил на дне моря и погружаться в своеобразную спячку, поднимаясь для дыхания лишь раз в несколько часов. Несмотря на огромные размеры, архелоны должны были откладывать яйца на суше — среди современных черепах нет живородящих видов. Действительно, не так давно в прибрежных отложениях Внутреннего Мелового Моря найдены следы (отпечатки) гнездовий гигантских морских черепах, вероятно архелонов. Есть предположение, что черепахи приплывали во Внутреннее Море именно для размножения. Питание архелона, возможно, напоминало диету современных кожистых черепах — медузы, ракообразные, возможно, аммониты. Архелон — один из объектов криптозоологии. Сведения о встречах в различных морях со сверхгигантскими (до 12 метров длиной!) черепахами иногда пытаются объяснить выживанием архелона. Но существование так называемого «Отца Всех Черепах» вообще маловероятно, поскольку черепахи должны откладывать яйца на суше и его должны были бы заметить. Выживание же архелона вообще представляется невероятным, поскольку этот род не дожил даже до конца мела. Впрочем, другие протостегиды известны до самой мел-палеоценовой границы. Unlike most modern turtles, Archelon did not have a solid shell, but instead had a skeletal framework supporting a leathery or bony carapace. Other distinguishing features include a pointed tail, a narrow skull, a relatively narrow, high-vaulted shell, and a pronounced overbite. The live weight of an Archelon ischyros is estimated at more than 2,200 kg (4,900 lb). They probably had a very strong bite, and were optimized for feeding on pelagic mollusks such as squid. The specimen exhibited by the Museum of Natural History in Vienna is estimated to have lived to be a century old, and may have died while brumating on the ocean floor. However, brumation in reptiles is a response to cold weather and it is unlikely that the Western Interior Sea was ever that cold. ( Read More ) Репродукции (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7):
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Ископаемые останки и реплики (1, 2, 3, 4, 5):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, бесщитковые, диапсиды, протостегиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |
| 08:30 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Manchurochelys Manchurochelys is an extinct genus of turtle in the order Paracryptodira. It existed during the early Cretaceous of what is now northeast China. It has been found in the Jianshangou Bed of West Liaoning's Yixian Formation. However, it is a rarely found fossil. Manchurochelys was first named by Endo and Shikama in 1942, and contains the single species, M. manchoukuoensis (sometimes misspelled M. manchouensis). A second species, M. liaoxensis, was named in 1995 but was later shown to be a species of Ordosemys. Manchurochelys was a relative of the modern-day snapping turtle. It has been occasionally placed in the family Sinemydidae, although it is said to more likely belong in the family Macrobaenidae. Ordosemys is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Cretaceous period. Скрытоше́йные черепа́хи (Cryptodira) — самый большой подотряд черепах, объединяющий 6 семейств. Помимо трёх семейств, включающих по 1—2 вида, сюда входят также два самых обширных семейства пресноводных черепах (85 видов) и сухопутные черепахи (37 видов). Общее число видов скрытошейных достигает 148, то есть 2/3 всех черепах. Распространены по всему жаркому и умеренному поясу земного шара кроме Австралии, в степной полосе России и на Кавказе распространены болотные черепахи. Скрытошейные черепахи способны втягивать шею и голову под панцирь, изгибая шею S-образно в вертикальной плоскости. В связи с этим шейные позвонки лишены поперечных отростков (или они рудиментарны). У некоторых видов, имеющих очень крупную голову, под панцирь втягиваются только шея и затылок. Тазовые кости не сращены с панцирем. Пластрон покрыт 11—12 роговыми щитками. К этому подотряду относятся слоновые черепахи длиной до 1,2 метров.
Ископаемые останки и реплики (1, 2, 3, 4):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Мел, анапсиды, диапсиды, скрытношейные, черепахи |