[Recent Entries][Archive][Friends][User Info]
February 13th, 2012
| February 13th, 2012 | |
|---|---|
| 05:56 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
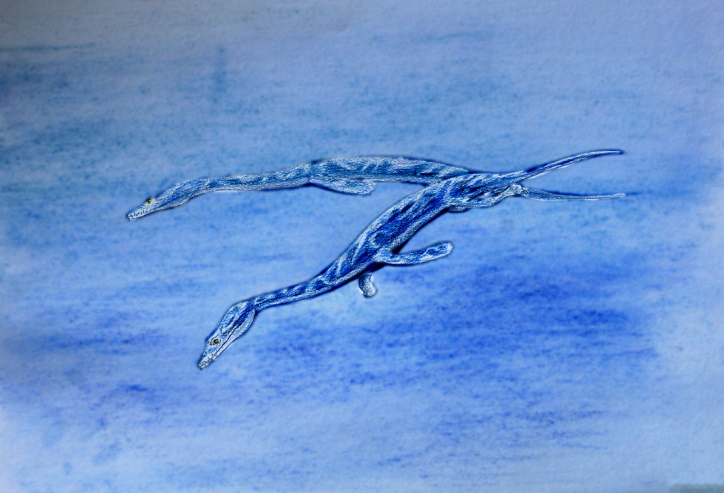
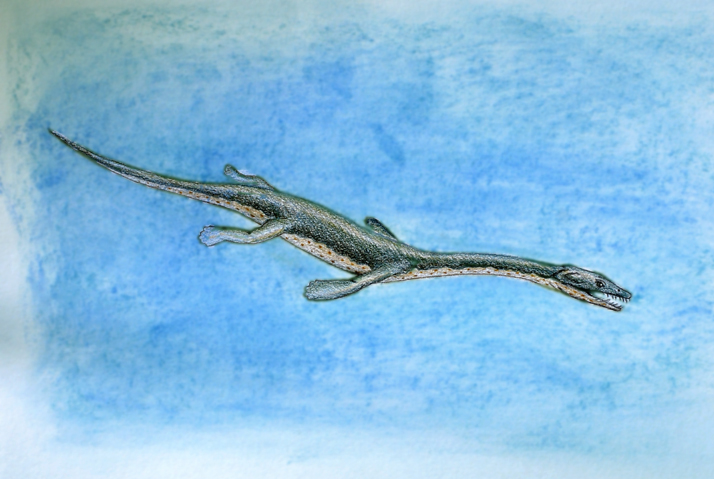
Ceresiosaurus Ceresiosaurus, meaning "Lizard of Ceresio" (Ceresio is the name of the Lake Lugano, in Switzerland), is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile belonging to the nothosaur order. Its fossils have been found in Europe, and was named by Bernhard Peyer in 1931. Ceresiosaurus lived during the Anisian stage of the middle Triassic. Olivier Rieppel suggested that Ceresiosaurus is a synonym of Lariosaurus. Ceresiosaurus was much more elongated than its relatives, reaching 4 metres (13 ft) in length, and had fully developed flippers with no trace of visible toes. It had multiple elongated phalanges, making the flippers much longer than in most other nothosaurs, and more closely resembling those of the later plesiosaurs. Ceresiosaurus also had the shortest skull of any known nothosaur, which further increased its resemblance to plesiosaurs. Although possessing a long neck and tail, Ceresiosaurus may not have swum by undulating its body. Analysis of the bone structure of the hips and powerful tail suggest that it instead propelled itself through the water much like a penguin. The evidence of pachypleurosaurs in the preserved stomach of Ceresiosaurus remains lend credence to the theory of it being a fast swimmer.
Размеры тела в сравнении с человеком:
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, диапсиды, завроптеригии, лепидозавроморфы, нотозавры |
| Time | Event |
| 06:27 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
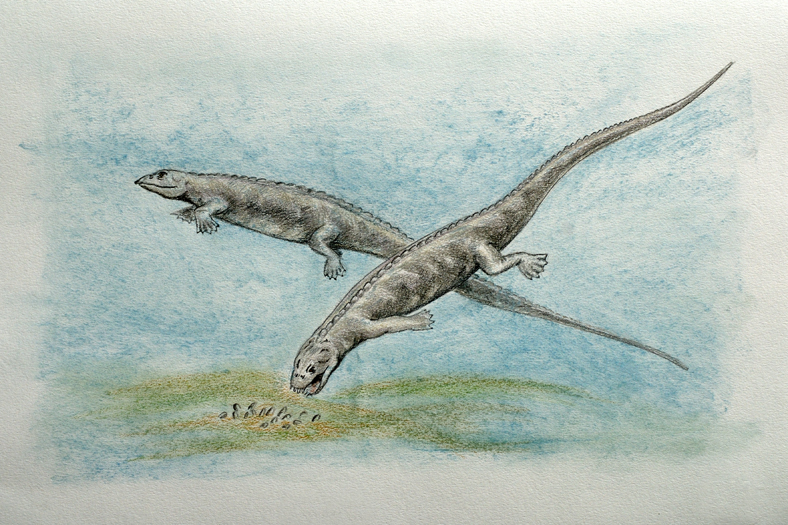
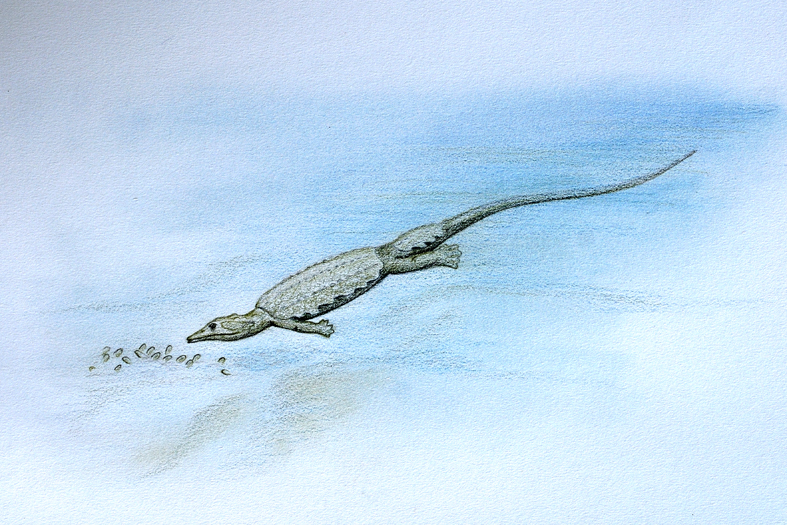
Lariosaurus Lariosaurus is an extinct genus of nothosaur from the Triassic period of northern Italy. With a length of just 60 centimetres (2.0 ft), it was one of the smallest known nothosaurs. It was named in 1847 by Curioni, its name meaning "Lizard (from Lake) Lario". The nothosaur Eupodosaurus, initially classified as a stegosaurian dinosaur, is now considered synonymous with Lariosaurus. For a nothosaur, Lariosaurus was primitive, possessing a short neck and small flippers in comparison to its relatives. This would have made it a relatively poor swimmer, and it is presumed to have spent lots of time on dry land, or hunting in shallows. Lariosaurus unique among nothosaurs because its front legs were adapted into paddles, while the back legs remained five-toed. Further, based on skeletal findings of immature lariosaurs inside the adults, Lariosaurus is believed by many to be viviparous, or able to bear live young. Another Lariosaur skeleton was found with two juvenile placodonts of the Cyamodus genus in its stomach, giving an indication of its diet.
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6):
( Далее ) Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, диапсиды, завроптеригии, лепидозавроморфы, нотозавры |
| Time | Event |
| 07:07 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
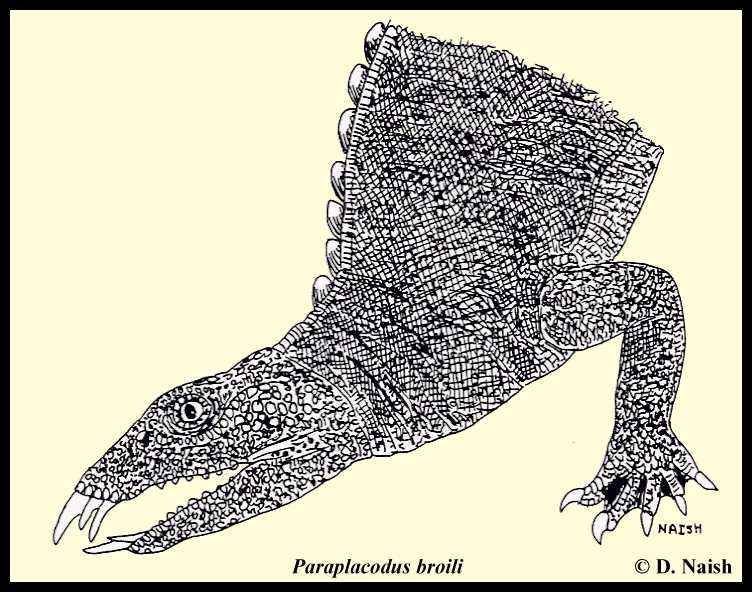
Paraplacodus Paraplacodus was a Placodont from the middle Triassic period, during the Anisian to Ladinian stages. The fossils were uncovered in Northern Italy and the species was named in 1931 by Bernhard Peyer. Paraplacodus means "Almost Placodus", and thus far only one species, P. broilli, has been identified, although as the name suggests, it was similar to Placodus, and also bore a strong resemblance to Saurosphargis. Like all known Placodonts, Paraplacodus was an aquatic reptile that fed almost exclusively on shellfish. Most known Placodont species can be divided into two groups - the unarmored placodontoids, which would resemble a large, scaly, tooth-filled newt, or the armored cyamodontids, which would resemble a heavily-armored turtle; Paraplacodus would have been in the newt-like family, but grew to a length of 1.5 meters (4.5 feet). The jaws of Paraplacodus were adapted to eat shellfish, with three pairs of protruding teeth in the top row and two rows of protruding teeth in the front of the jaw, with rounded crushing teeth in the upper and lower jaws. Thick ribs formed a box-like ribcage with an almost-square cross-section, which enabled Paraplacodus to remain close to the seabed while hunting for food. Плакодонты (Placodontia) — отряд ископаемых морских пресмыкающихся надотряда Sauropterygia, живших в триасовом периоде на территории Европы, Азии и Африки. Название означает «плоские зубы». Плакодонты не являлись полностью водными животными, в некоторых отношениях они были более приспособлены к жизни на суше, однако, по всей видимости, существенную часть времени проводили в теплых водах прибрежной полосы. Их рацион составляли разнообразные моллюски и ракообразные, которых они отрывали от морского дна (в этом им помогали ковшевидные челюсти, снабженные мощными мышцами, и шесть конических острых передних зубов). А 14 тупых, плоских коренных зубов позволяли перемалывать раковины, превращая их в кашицу. Длинный хвост помогал проталкивать под водой тело. Плакодонты, вероятно, были легкой добычей для хищников, поскольку медленно передвигались. Поэтому у многих из них на спине развился защитный панцирь. У некоторых панцири были довольно широкими и походили на черепашьи, но плакодонта нельзя счатать родственником черепахи. Одинаковые панцири выработались из-за обитания в одинаковой среде. Этот процесс называют конвергентной эволюцией. Плакодонты вымерли, вероятно, примерно 200 миллионов лет назад вместе с другими животными, исчезнувшими во время наступившего тогда массового вымирания. По одной теории это вымирание произошло из-за широкого распространения динозавров, по другой из-за перехода от обильных осадков к гораздо более засушливому климату.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, диапсиды, завроптеригии, лепидозавроморфы, плакодонты |
| Time | Event |
| 07:17 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Cyamodus Cyamodus was a placodont, known from fossil remains discovered in Germany, in the early-to-mid-19th century and was named by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer, in 1863. The fossils have been dated to the Triassic Period, from the Anisian to Ladinian stages. Cyamodus was 1.3 meters (4 feet) long. Cyamodus was a heavily armored swimmer that fed mainly on shellfish that it was specialized to uproot and crush with its powerful jaws. The body of Cyamodus, specifically the armor, has been described as possessing a turtle-like flatness. The shell was a two-part carapace on the upper surface of the body. The larger half covered Cyamodus from the neck to the hips and spread out flat, almost encompassing the limbs. The second, smaller plate covered the hips and the base of the tail. The shells themselves are covered in hexagonal or circular plates of armor. The skull is heart-shaped and broad. Thus far, five species of Cyamodus have been identified - C. rostratus, C. munsteri, C. tarnowitzensis, C. hildegardis, and C. kuhnschneyderi. Cyamodus is the type genus of the family Cyamodontidae.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, диапсиды, завроптеригии, лепидозавроморфы, плакодонты |
| Time | Event |
| 07:40 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
Psephoderma Psephoderma (meaning 'pebbly skin') is a genus of placodont that was very similar to its relatives Placochelys and Cyamodus. Psephoderma had a flattened skull and a narrow, straight rostrum. Inside this skull, embedded in the jaws, were rounded teeth specialized for crushing the shellfish it ate. Unlike most placodonts, Psephoderma had a carapace that was divided into two pieces, one on the shoulders and back, another on the rear end. Psephoderma grew to 180 cm long and lived in the Late Triassic (Norian), about 210 million years ago. It was one of the last placodonts to live.
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, диапсиды, завроптеригии, лепидозавроморфы, плакодонты |
| Time | Event |
| 07:45 pm [industrialterro] [Link] |
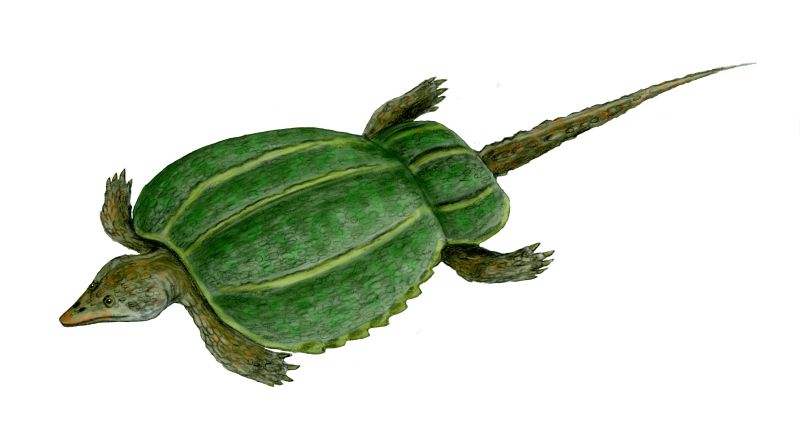
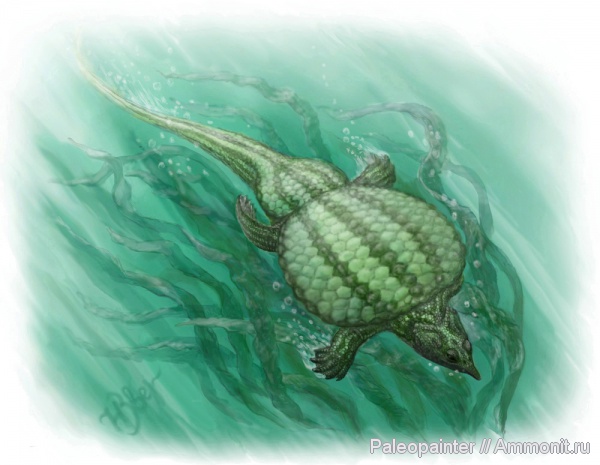
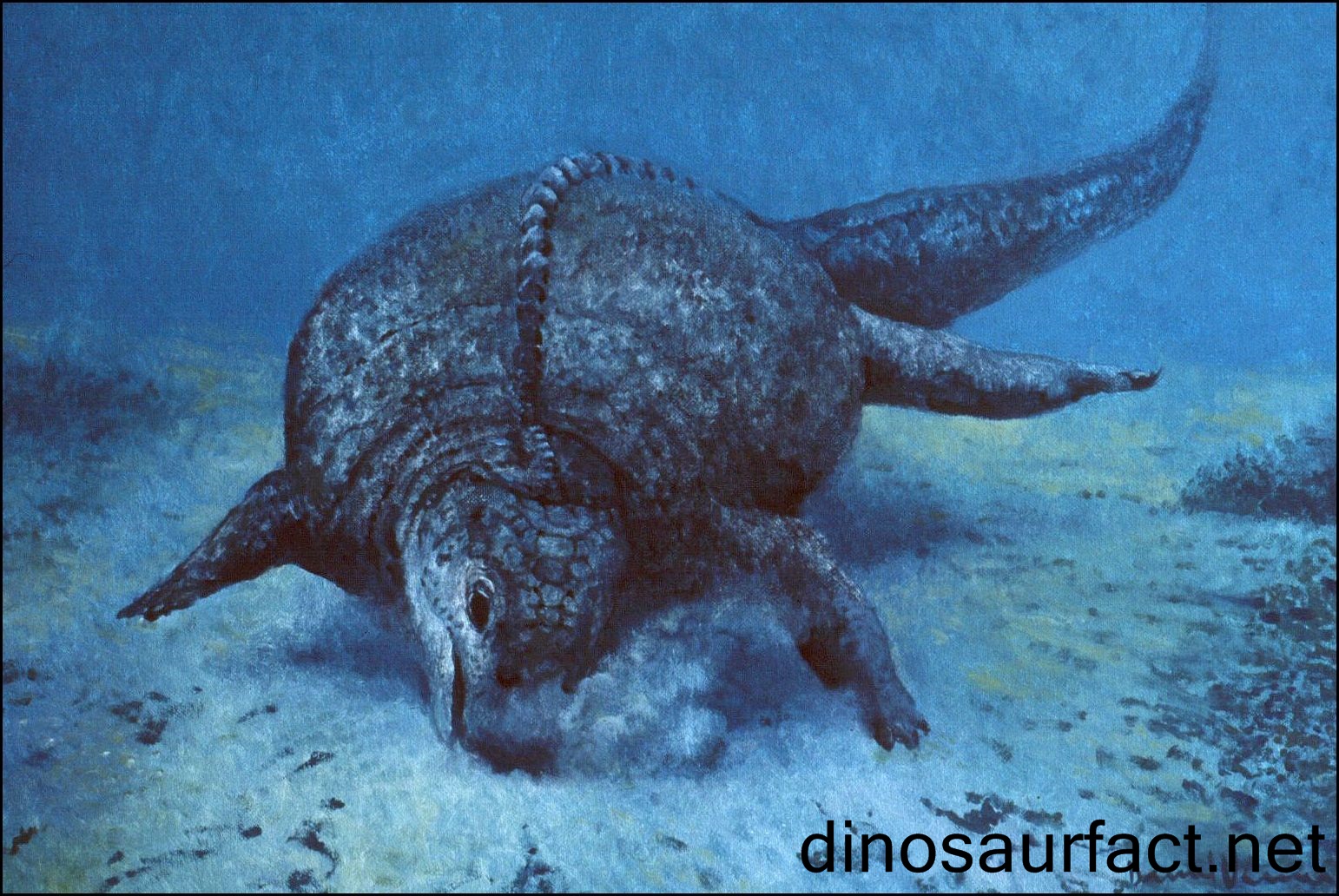
Henodus Henodus chelyops ("Turtle-Faced Single Tooth") was a placodont of the Late Triassic period during the early Carnian age. Fossils of Henodus chelyops were found in Tübingen, Germany. It was around 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length. Henodus was the placodont that had the greatest (albeit superficial) resemblance to a turtle. Like turtles, it had a shell formed from a plastron on the underside and a carapace on top. The carapace extended well beyond the limbs, and was made up of individual plates of bony scutes covered by plates of horn. However, the shell was composed of many more pieces of bone than that of turtles, forming a mosaic pattern. The armor was fused to its spine, and its limbs were situated in normal positions, unlike the turtle, where they are located inside the ribcage. The weak limbs of Henodus suggest it spent little, if any time on land. Henodus chelyops also had a single tooth on each side of its mouth, though the remaining teeth were replaced by a beak. These teeth were flat to crush bottom dwelling shellfish. The head was squared-off at the front, just ahead of the eyes. Henodus is the only placodont thus far found in non-marine deposits, suggesting it may have lived in brackish or freshwater lagoons. Henodus - один из самых замечательных плакодонтов. Это курьезное пресмыкающееся длиной свыше 1 метра жило в триасе, его остатки найдены близ западногерманского города Тюбинген. Генод имел прямоугольную голову и неуклюжее приземистое туловище, целиком покрытое могучим панцирем, подобным черепашьему, у него сохранилось лишь четыре Геноды обитали в солоноватоводных, спокойных лагунах позднего триаса Центральной Европы. Их короткое (до 1 м) тело было заключено в широкий панцирь до области таза, конечности небольшие, тонкие, а относительно длинный хвост был покрыт костными пластинами. Череп почти прямоугольный. В задней части неба генода по обеим сторонам имелось по одному уплощенному зубу. От этих зубов до переднего режущего края морды вели бороздки, предположительно вмещавшие хитиновые пластинки. Возможно это был цедильный аппарат и генод питался мелкими придонными организмами.
Ископаемые останки (1, 2, 3, 4, 5):
Tags: Вымершие рептилии, Триас, диапсиды, завроптеригии, лепидозавроморфы, плакодонты |
| Previous Day | 2012/02/13 [Archive] |
Next Day |